Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
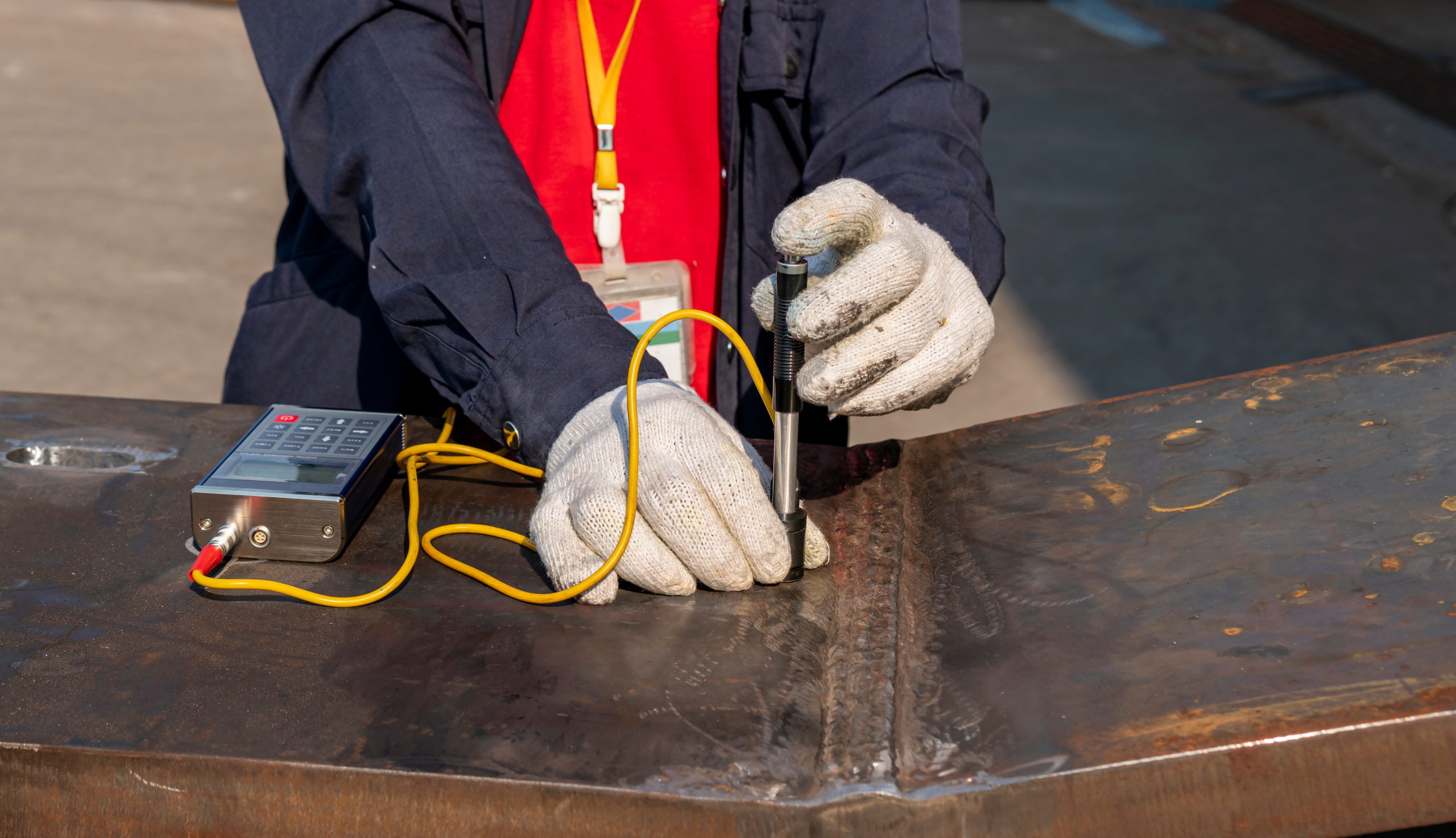
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) refers to inspection methods used to evaluate the integrity of materials or welds without causing damage to the part.
Common NDT techniques in steel fabrication include:
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): using high-frequency sound waves to detect internal weld flaws or measure thickness;
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): applying magnetic fields and iron particles to reveal surface cracks in ferromagnetic materials
Dye Penetrant Testing (PT): using dye and developer to find fine surface cracks
Radiographic Testing (RT): using X-rays or gamma rays to image internal structures of welds for porosity, lack of fusion, etc.
NDT is often required for critical welds (for example, full penetration welds on load-bearing columns or moment connections) per codes or client specs, as it ensures weld quality without cutting apart the member.
Small steel fabrication shops might perform some NDT in-house (MT and PT are relatively simple), but often they hire certified Level II or III technicians or labs for UT or RT.
NDT results can trigger repairs if defects are found. Hence NDT is a QA/QC tool to ensure the final structure will perform as intended.
Embracing NDT helps a shop qualify for higher-tier work (like DOT or high-rise jobs) and reduces the liability from hidden defects.
It’s also part of adhering to standards like AWS D1.1, which specify NDT acceptance criteria.