Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)
What is Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)?
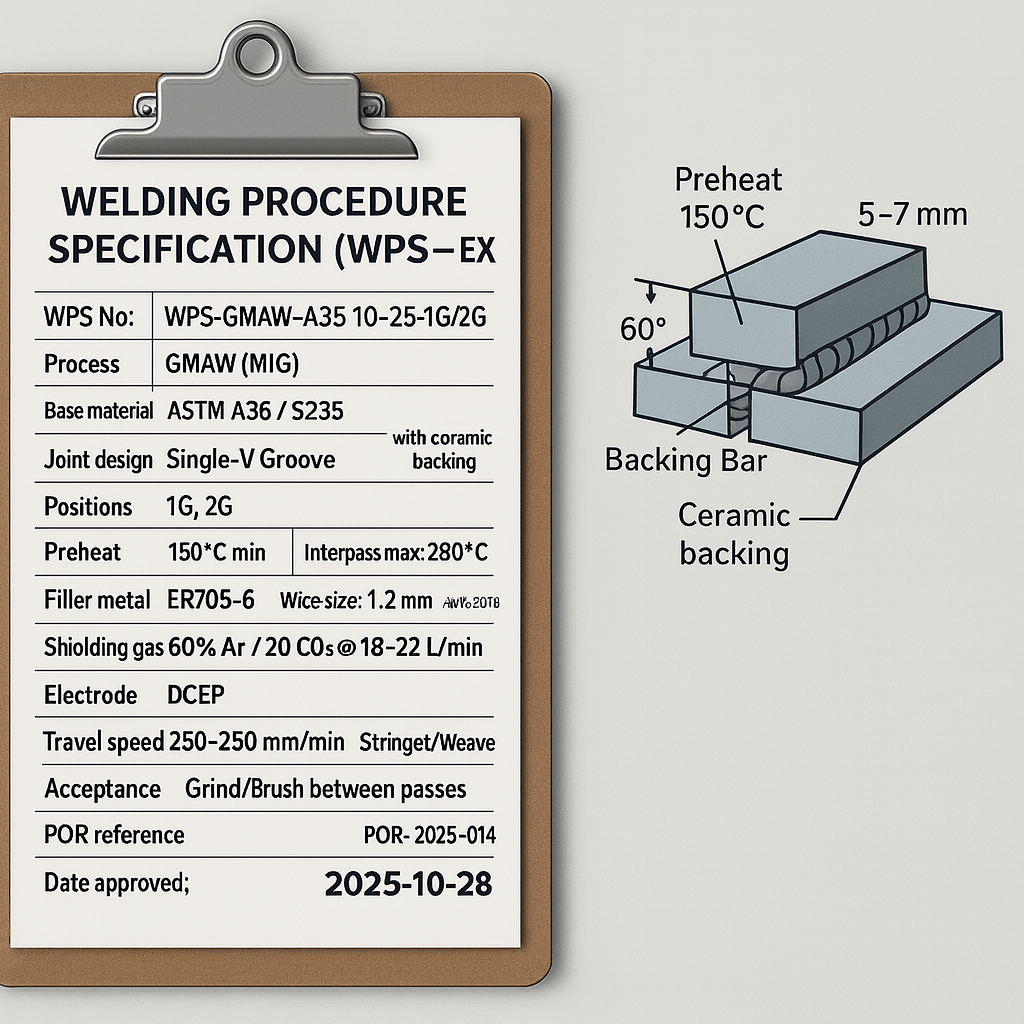
A Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) is a formal written document that describes how a weld is to be made, in order to ensure repeatable, high-quality welds that meet code requirements.
It includes details like the welding process (for example, SMAW, GMAW), base material grades and thickness range, joint design, position, preheat temperature, welding current and polarity, filler metal type and size, shielding gas, and more – all the “recipe” variables for a specific weld application.
WPSs are typically qualified by testing (weld samples are made and subjected to mechanical tests) and often are required by standards such as AWS D1.1 (Structural Welding Code – Steel) or ISO 15614 before production welding begins.
In a small fab shop, having WPSs for the common weld joints (such as flange-to-web fillet welds, full penetration groove welds in columns) is both a compliance and quality measure. Welders then follow the WPS to know, for example, to use E7018 electrodes at a certain amperage with 150°C minimum preheat on a given thick plate weld.
A supporting document called a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) proves that the WPS parameters produce a sound weld (by lab test results).
By adhering to WPSs, a shop ensures consistency across different welders and jobs, reduces the risk of weld failures, and satisfies client and regulatory requirements.
A WPS also a training and assessment tool. Welders are tested on their ability to follow and weld within the WPS limits (often through Welder Qualification tests).