Galvanization involves coating a metal with zinc to prevent corrosion and protect it from the environment. This common practice in manufacturing and engineering brings many benefits to using galvanized materials. But what about sustainability? Is galvanizing environmentally friendly? Let’s take a closer look.
What is Galvanization?
Hot-dip galvanizing is the process of applying a thin layer of zinc to steel or iron to protect it from corrosion. This protection is vital because it helps to extend the lifespan of steel or iron products, which can be exposed to a lot of wear and tear over time.
The galvanization process is relatively simple: first, the surface of the metal is cleaned to prepare it for the zinc coating. Next, a layer of zinc is applied, typically using an electrochemical process. Finally, the zinc-coated metal is cooled and passivated, which helps to protect it from further corrosion.
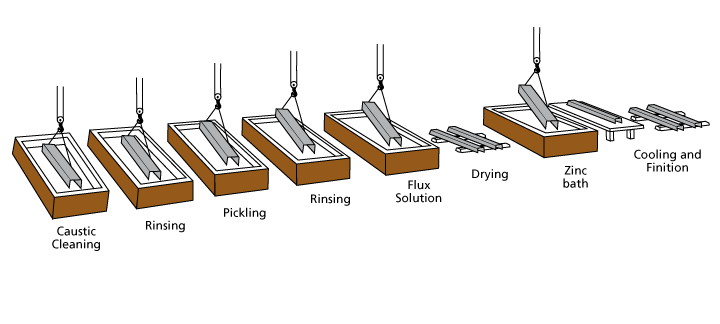
Image credit: https://www.galvanisationquebec.com
Top 6 Benefits of Galvanizing:
- Self Healing Ability
The zinc layer that is applied during galvanization acts as a barrier to oxygen and water, preventing the steel or iron beneath from rusting – up to 5 mm. But in the event that the zinc layer is damaged and exposes the metal to the elements, the zinc will actually sacrifice itself to protect the steel or iron. This “self-healing” ability is one of the main benefits of galvanization.
- Corrosion Protection
Galvanized materials are highly resistant to corrosion, which means they will last longer and require less maintenance over time as compare to painting. This is especially important in industries where steel or iron products are exposed to harsh environments, such as marine applications.
- Increased Service Life
The increased lifespan of galvanized materials is one of the main reasons why they are so popular in manufacturing and engineering. By extending the service life of products, businesses can save money on replacement costs and reduce their environmental impact.
- Cost-Effective Finishing Option
Galvanization is a relatively inexpensive finishing option compared to other methods, such as paint or powder coating. This makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to save money.
- Durability
Galvanized materials are incredibly durable and can withstand a lot of wear and tear. This is because zinc is a solid metal that is not easily damaged.
- High-Speeded Process
Galvanization is a fast process that can be completed in a matter of hours. This is important for businesses that need to quickly get products out the door.

How galvanizing is Sustainable?
Galvanizing is a sustainable process that is energy efficient and recyclable. The method of galvanizing uses natural resources that are replenished quickly. This makes the process economical as well as environmentally friendly.
In addition, galvanizing is a reliable method of protecting steel from corrosion. It can be used in various applications, including in construction and transportation. As a result, galvanizing is integral to making our world more sustainable.
What is galvanized steel used for?
Galvanized steel, in particular, is often what is used in modern “steel frame” buildings. Galvanized steel is also used to create structures like balconies, verandahs, staircases, ladders, walkways (galvanized handrails), and more. Galvanized metal is the ideal choice if your project will live outside after it’s done
Types of Galvanizing
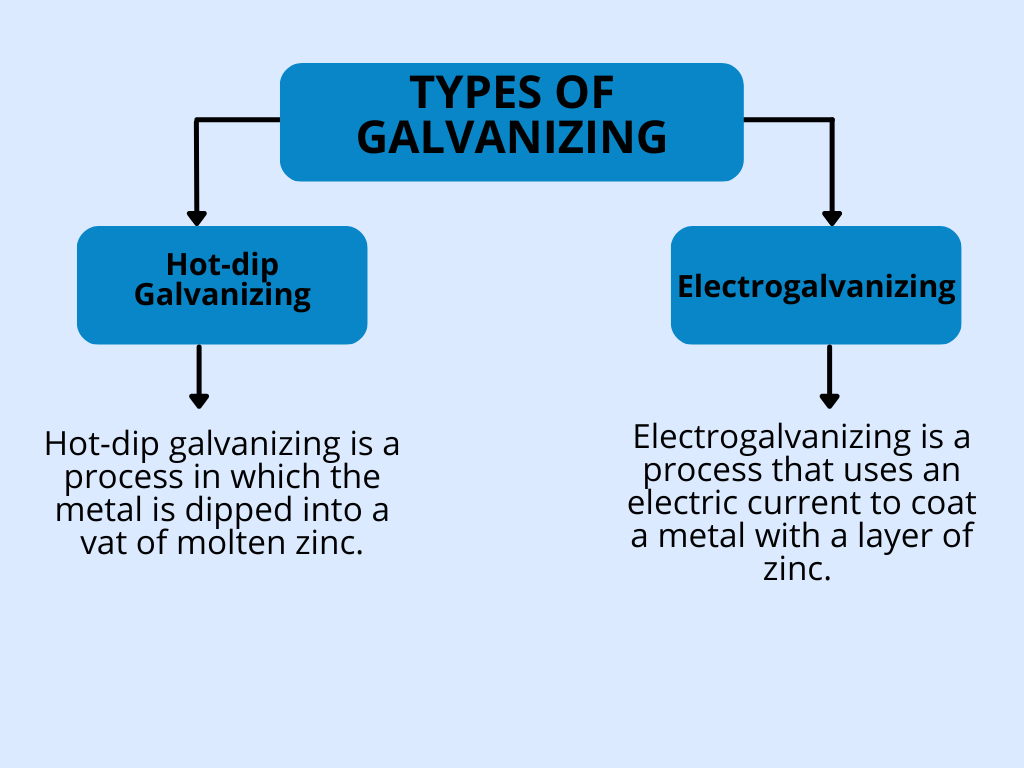
Two types of galvanizing.
There are two types of galvanizing processes: hot-dip galvanizing and cold-dip galvanizing.
Hot-dip Galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing is a process in which the metal is dipped into a vat of molten zinc. This provides a thick, durable coating that offers excellent protection against corrosion.
Electrogalvanizing
Electrogalvanizing is a process that uses an electric current to coat a metal with a layer of zinc. In this process, the steel is dipped in a solution that contains zinc and an electrolyte, such as sulfuric acid. An electrical current is passed through the solution, causing the zinc to be deposited onto the steel. It is often used on metals that will be exposed to the environment, such as car parts and steel structures.
Both hot-dip and electrogalvanizing are used to protect steel from corrosion. However, hot-dip galvanizing is more commonly used because it provides a thicker, more durable coating.
Book a 60-minute demo to see
how eziil mrp solution works for you
Applications of Galvanized Steel
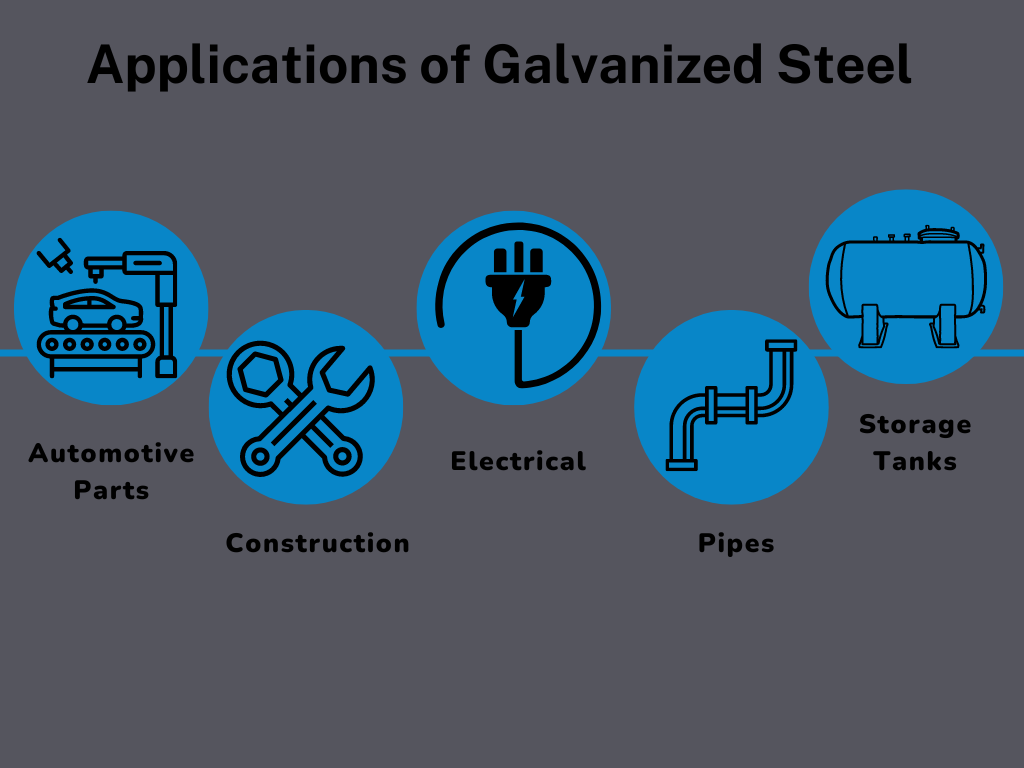
Variety of applications of galvanized steel
Galvanized steel is used in a wide variety of applications. Some of the most common include:
1. Automotive Parts
Galvanized steel is often used to create car parts, such as exhaust systems. The zinc coating helps to protect the steel from rust and corrosion.
2. Construction
This type of steel is commonly used in the construction industry to create scaffolding, support beams, and other structures. A zinc coating is often applied to protect the structural steel from weather conditions.
3. Electrical
It is often used to create electrical components, such as power lines and transformers. The zinc coating helps to protect the steel from corrosion and electrical shorts.
4. Pipes
Galvanized steel is typically utilized to create pipes and tubing. Pipes are surface treated with a zinc coating that helps prevent rust and corrosion in harsh industrial environments and weatherly conditions.
5. Storage Tanks
It is used to create storage tanks. Storage tanks are required to store fluid for long durations, which increases the chances of rusting and corrosion. To prevent them from the hazard of rusting or corrosion, zinc coating is found to be a solution.
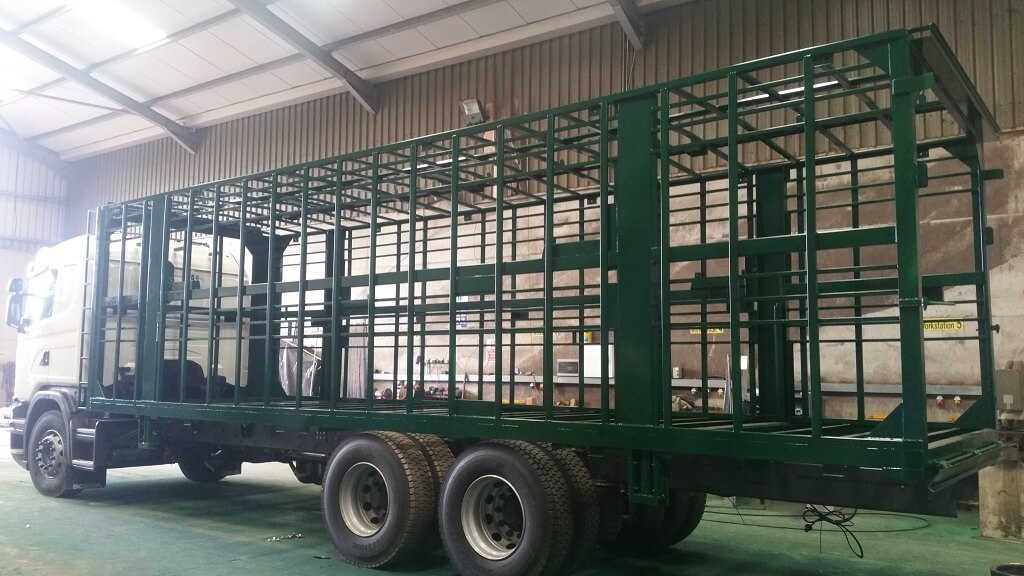
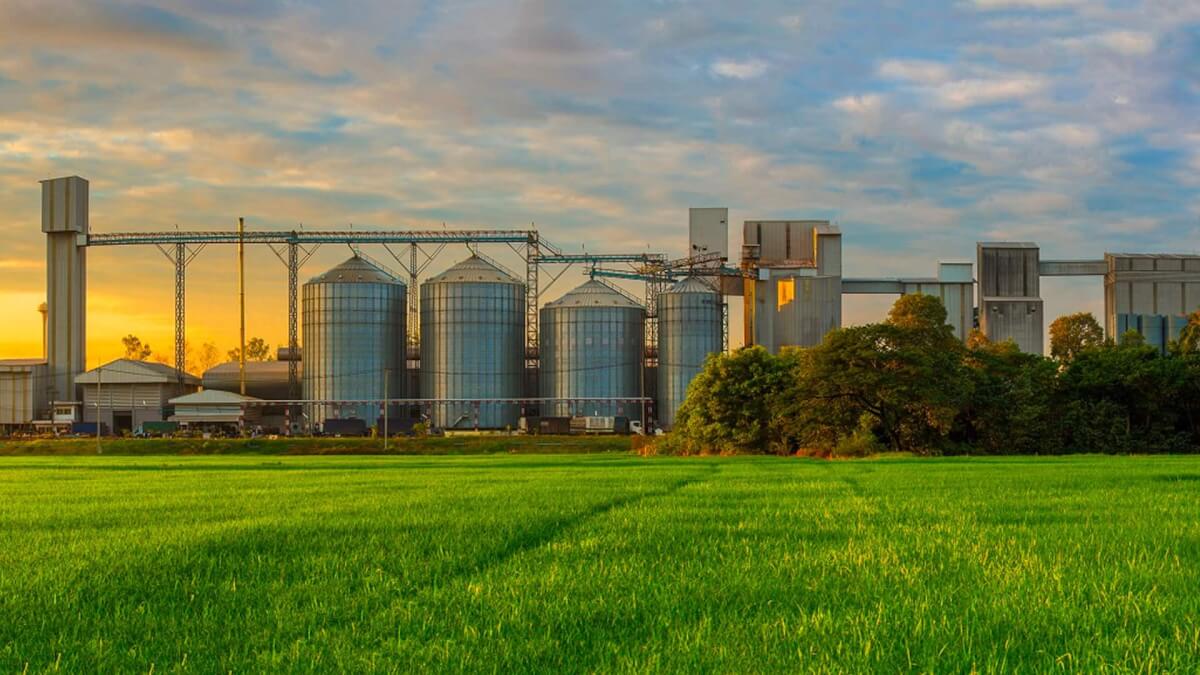


Applications in everyday life – storage tanks, trailers framework and electrical power poles.
Picture credits: https://www.azz.com, https://galco.ie, http://www.steeltowerchn.com
Design Requirements and
Limitations for Galvanization
When choosing a galvanization method, it is essential to consider the specific requirements and limitations of the project. Some essential requirements include the following:
Design Requirements:
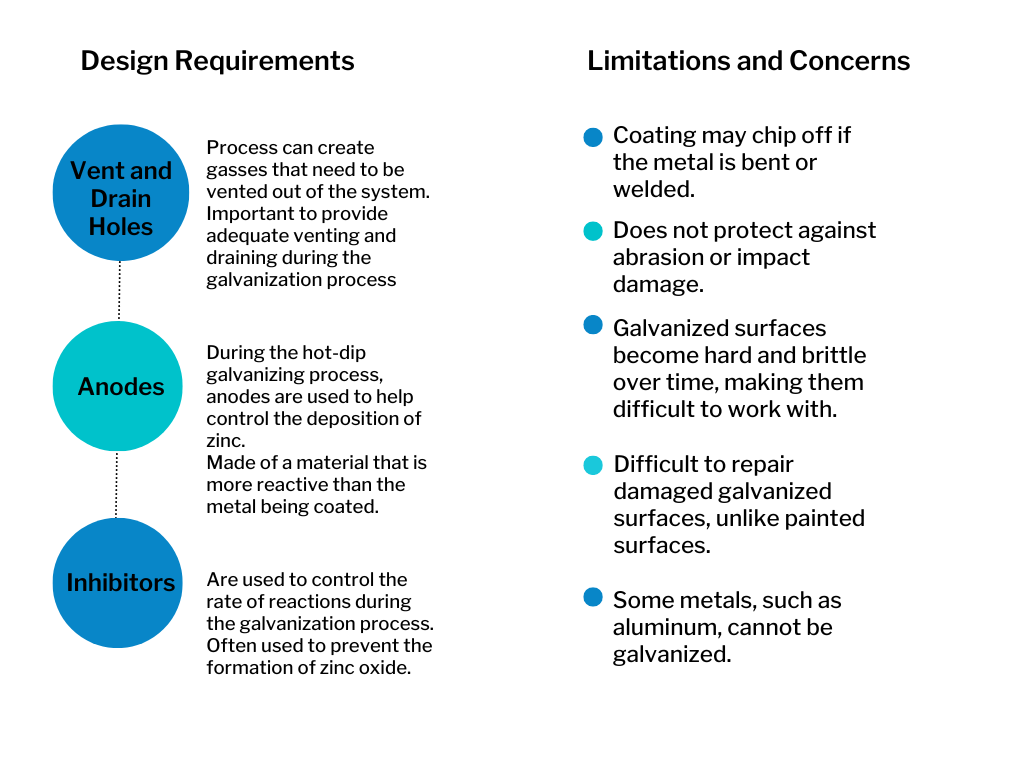
- Vent and Drain Holes – The zinc coating process can create gasses that need to be vented out of the system. It is important to provide adequate venting and draining during the galvanization process.
- Anodes – During the hot-dip galvanizing process, anodes are used to help control the deposition of zinc. They are made of a material that is more reactive than the metal being coated. This helps to prevent the formation of zinc oxide on the surface of the metal.
- Inhibitors – Inhibitors are used to control the rate of reactions during the galvanization process. They are often used to prevent the formation of zinc oxide.
Limitations and Concerns:
- The zinc coating may chip off if the metal is bent or welded.
- The zinc coating does not protect against abrasion or impact damage.
- It can be challenging to control the thickness of the coating, and there is a risk of damaging the underlying metal if the process is not carefully controlled.
- In electro-galvanization, it is less likely to damage the metal, but it produces a thinner coating that may not be as durable as a hot-dip coating.
- Galvanized surfaces become hard and brittle over time, making them difficult to work with. Some metals, such as aluminum, cannot be galvanized.
- It is difficult to repair damaged galvanized surfaces, unlike painted surfaces.
Is carbon dioxide corrosive to steel? Carbon dioxide in aqueous solution is highly corrosive and can cause significant damage to steel designs. Such conditions arise in pipes used in a variety of applications, especially within the petrochemical industry.
Conclusion
So what is galvanization? Simply put, it’s a process that coats steel with a layer of zinc. The benefits of galvanizing are vast, and sustainability is one of its key features. We’ve outlined some of the top benefits of galvanizing and how this process is one of the most sustainable finishes available.
Eziil is MRP software for steel fabricators. We offer a complete suite of software solutions that enable our customers to streamline their operations, improve productivity, and increase profitability.
Whether you’re looking for a simple way to improve your project management or need a comprehensive solution for your entire operation, Eziil is the right partner. Book a demo today to learn more about how we can help you take your business to the next level.