You might be wondering to know about the metal forming process. Wait no more! We have developed an ultimate guide to educate you about some basic metal forming processes. We will also look closely at their advantages, applications, and the most suitable metals for metal forming.
By the end of 6 minutes read, you will better understand the basics of metal forming and decide which process is best for your needs.
So without further ado, let’s get started!
What is Metal Forming?
Metal forming is the process of shaping a piece of metal into the desired shape. The process can be done through various methods, including roll forming, bending, extrusion, forging, and many more. It is an important manufacturing process because it allows creating metal parts of various shapes and sizes. The process is also relatively efficient and can be used to create large structural metal parts with high accuracy. As a result, metal forming is an essential part of the manufacturing industry.
Basics of Metal Forming Process
Generally speaking, “metal forming” refers to a wide range of production procedures. But the transformation of raw metal stock into a finished item is the one feature all metal forming procedures have in common.
- Cold Working Process
In the cold working process, the metal is plastically deformed to achieve the desired shape. The deformation is done at room temperature and does not involve the addition or removal of material.
- Heat Treated Process
Besides cold working, the metal may also be heat treated in a metal forming process. By heating and cooling metals in specific ways, it is possible to change their physical and mechanical properties. The most common application of heat treatment is to create complex forms that can not be achieved in the cold state. However, heat treated process can also be used to make steel more ductile and wear resistant.
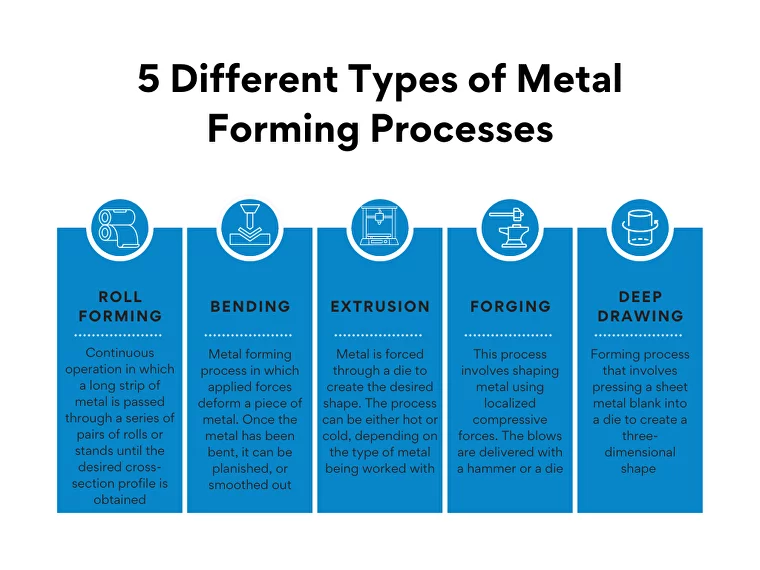
5 Different Types of Metal Forming Processes
Although there are many types of metal forming processes, they can be broadly classified into five main categories:
- Roll Forming
It is a continuous operation in which a long strip of metal (typically coiled steel) is passed through a series of pairs of rolls or stands, each set performing only an incremental part of the bend until the desired cross-section profile is obtained. Roll forming is performed at room temperature and can be used to form metals into a large variety of different shapes and sizes.
How Can Material Manufacturers and Steel Fabricators take Advantage of Roll Forming?
You must consider how steel fabricators and material manufacturers can take advantage of roll forming. Material manufacturers can take advantage of roll forming by using it to produce parts with different physical or mechanical properties. For example, they can use roll forming to produce parts that are more wear-resistant or have a higher strength-to-weight ratio.
In addition, steel fabricators can use roll forming to produce parts with more complex geometry. Fabricators usually have to work with a variety of different metals, including both cold-rolled and hot-rolled metals.
But what if there was a way to use roll forming to create parts from both types of metals?
Well, there is!
In fact, many steel fabricators have already adopted this method and are using it to create special profiles. Roll forming is slightly used in the fabrication industry however; bending is the more dominant method. Fabricators generally use roll-formed products like sheet metal; I, U & H profiles, circular and rectangular hollow sections. These hot-formed products are then fabricated into strut channels, metal door frames, automotive body panels, solar racking, etc.
Advantages:
The advantages of roll forming over other metal forming processes include:
- Ability to produce complex shapes with minimum tooling.
- Form metals with high strength-to-weight ratios.
- Versatility in forming a wide range of different metals.
- A continuous process that leads to high production rates.
- Generates little scrap.
- Easy to handle.
Disadvantages:
The process also has some disadvantages, including the following:
- Limited to metals that can be cold-rolled.
- Not well suited for metals with high yield strength.
- Bending
It is a metal forming process in which applied forces deform a piece of metal. The force required to bend the metal is determined by the material’s flexibility, thickness, and radius of curvature. Once the metal has been bent, it can be planished, or smoothed out, to remove any imperfections.
Bending is often used to create complex shapes from sheet metal, such as curves and corners. It can also be used to join two pieces of metal together. The metal must be heated to the proper temperature for a hassle-free process. This allows the molecules in the metal to become more pliable, making it easier to deform. Bending can be done by hand or machine.
Advantages:
Let’s talk about the advantages of bending first.
- Bending is relatively simple and does not require the use of expensive equipment.
- It can be done by hand or using a machine.
- It is one of the most economical metal forming processes.
- Parts developed through bending require less tooling and post-processing operations.
- It offers high accuracy and precision.
Disadvantages:
- The process can only be used on metals that are ductile enough to be deformed.
- The process is not well suited for metals that are difficult to weld.
- Extrusion
In this metal forming process, a metal is forced through a die to create the desired shape. The process can be either hot or cold, depending on the type of metal being worked with. Extrusion is often used to create objects with a hollow center, such as pipes or tubing. The process can also create solid objects with a complex cross-sectional shape. As the metal is forced through the die, it takes on the shape of the opening.
This makes extrusion an ideal method for creating parts with a precise and consistent cross-sectional shape. In addition, extrusion can be used to create parts with varying cross-sectional shapes by using dies with multiple openings. The process can also create long, continuous lengths of material, making it ideal for plumbing or electrical wiring applications.
- Forging
After extrusion comes forging, this process involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer or a die. Forging is often categorized according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging, warm forging, or hot forging.
Cold forging (typically done below room temperature) avoids the workpiece’s annealing or heat-softening. Warm forging (performed at temperatures above room temperature) increases the ductility and toughness of the workpiece. Hot forging (performed at temperatures above recrystallization temperature) reduces surface roughness and scale formation on the workpiece.
- Deep Drawing
The process of deep drawing is a forming process that involves pressing a sheet metal blank into a die to create a three-dimensional shape. This process is often used to create low-profile cylindrical parts, such as components for the automotive and aerospace industries.
The sheet metal blank must be stretched beyond its elastic limit to achieve the desired shape. This can be achieved through an intricate die design and careful control of the blank’s material properties.
Book a 60-minute demo to see
how eziil mrp solution works for you
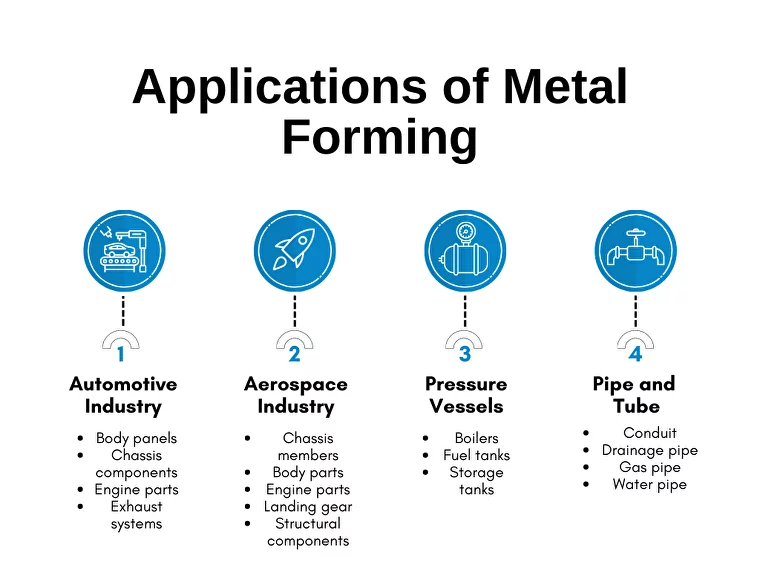
Applications of Metal Forming
Metal forming is used in various industries to create parts of various shapes and sizes. Some common applications include:
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is the largest consumer of metal products. The average car contains over 2,000 pounds (907 kilograms) of steel. The metal forming processes are used to create a variety of parts for cars, trucks, and other vehicles, such as:
- Body panels
- Chassis components
- Engine parts
- Exhaust systems
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry is another major consumer of metal products. Metal forming is used to create a variety of parts for airplanes, spacecraft, and other vehicles, such as:
- Chassis members
- Body parts
- Engine parts
- Landing gear
- Structural components
Pressure Vessels
Pressure vessels are containers that hold liquids or gases at high pressures. This metal forming process is also used to create a variety of pressure vessels, such as:
- Boilers
- Fuel tanks
- Storage tanks
Pipe and Tube
Pipes and tubes are often used to transport liquids or gases. A variety of pipes and tubes can be produced through this process, such as:
- Conduit
- Drainage pipe
- Gas pipe
- Water pipe
The process of metal forming is essential to the manufacturing of a variety of products. The automotive and aerospace industries are two of the largest consumers of metal products. In addition, pressure vessels and pipes are often made using metal forming processes.
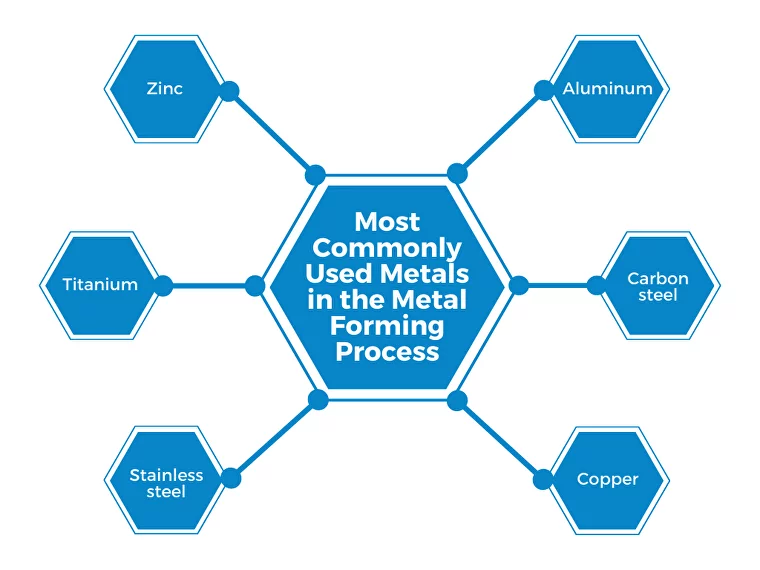
Most Commonly Used Metals in the Metal Forming Process
There are a variety of metals that can be used in the metal forming process. However, some metals are more commonly used than others. The most common metals used in metal forming are:
- Aluminum
- Carbon steel
- Copper
- Stainless steel
- Titanium
- Zinc
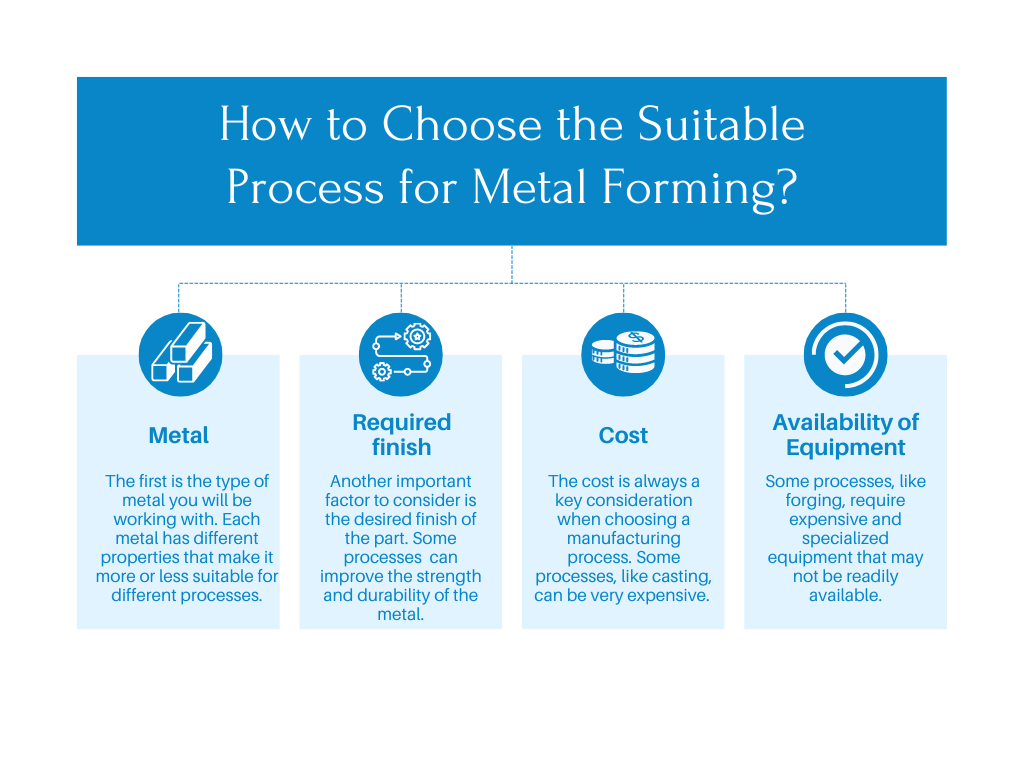
How to Choose the Suitable Process for Metal Forming?
If you are in the metal forming industry, determining the best process for your application is essential to ensuring a successful outcome. It would help if you considered a few key factors when choosing a process for your application.
- Metal
The first is the type of metal you will be working with. Each metal has different properties that make it more or less suitable for different processes. For example, soft metals like aluminum are often best suited for processes like stamping, while harder metals like steel may require more forceful processes like forging.
- Required finish
Another important factor to consider is the desired finish of the part. Some processes, like annealing, can improve the strength and durability of the metal, while others, like polishing, may be more focused on achieving a cosmetic finish.
- Cost
Of course, the cost is always a key consideration when choosing a manufacturing process. Some processes, like casting, can be very expensive, while others, like stamping, can be quite cost-effective.
- Availability of Equipment
Another important factor to consider is the availability of equipment. Some processes, like forging, require expensive and specialized equipment that may not be readily available.
Considering these factors, you can narrow your options and choose the best process for your needs.
Conclusion
So, that was the ultimate guide of metal forming processes. It’s important to choose the right process for your project, so hopefully, this guide will help you do that. Metal fabricators extensively use metal forming to fabricate several structural components.
Eziil is an efficient MRP system designed for metal fabrication companies. It provides real-time data on performance and also offers inventory management. You can also manage your purchase orders and can check real-time project margins from this software. If you have any questions about this MRP software, don’t hesitate to get in touch – Eziil Team would be happy to help. Thanks for reading!
References
Anon., n.d. Mechanical Education. [Online]
Available at: https://www.mechanicaleducation.com
Anon., n.d. Quest Tech. [Online]
Available at: https://questtech.ca/blog