Welding defects are flaws that can form at any stage of the welding process, and when they do, they can compromise the intended use of a weldment. They are deviations in size and shape from the technical and design requirements. Although some defects are allowed since they do not compromise set standards and quality, others are unacceptable.
Flaws that do not compromise the weld are called weld discontinuities. However, if too many of these discontinuities exist, they are classified as defects and are subject to rejection.
While it is virtually impossible to create a defect-free weld, welders must reduce the occurrence of defects to prevent material loss and maintain the intended quality. And since every welder’s goal is to avoid having their welds rejected, everyone should learn the types of defects that can happen and how to avoid them.

Why is it Essential to Avoid Welding Defects?
The primary reason to identify and prevent weld defects is the potential danger a poor-quality weld can pose since they are more likely to fail. The consequences of a weld failing might be merely the inconvenience of a pipe bursting in the bathroom. However, if the weld on a gas pipe should fail, the results could be catastrophic, including loss of life. The same is true of a structural weld in which a bad weld could injure or kill motorists crossing a bridge or workers in a high-rise office.
High-quality welds help improve the safety of structures and the innocent people who depend on them for their well-being. Most professional welders already understand that welding defects are about much more than aesthetics, and many of them are passing that message on to those new to the trade who have yet to realize the potential dangers of welding defects.
Welding defects can occur in many types of welding processes, including arc welding and gas metal arc welding (GMAW). One common welding defect is porosity, which is caused by gas pockets forming in the weld. This can be caused by improper shielding gas in gas metal arc welding or poor weld preparation in arc welding. Another common defect is lack of fusion, which happens when the welding wire fails to melt and fuse with the base metal. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including incorrect arc length or poor welding technique.
To minimize welding defects, it’s important to follow proper welding procedures and use the correct equipment. For example, maintaining the correct arc length is critical to achieving a high-quality weld. In GMAW, the welding wire and shielding gas must also be selected carefully to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, proper weld preparation is essential to ensure that the base metal is clean and free of contaminants.
In the manufacturing process, detecting and addressing welding defects is critical to ensuring the safety and reliability of the final product. This can involve using non-destructive testing techniques, such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing, to detect defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. By taking these steps to prevent and detect welding defects, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and safety.
Preventing Welding Defects: Factors to Consider in SMAW, FCAW, and SAW
Welding defects are a common problem in many types of welding processes, including shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), flux cored arc welding (FCAW), and submerged arc welding (SAW). One way to prevent defects is by selecting the appropriate filler metal for the welding process. Using the wrong filler metal can result in a weak or brittle weld that is prone to cracking or other defects.
Another factor to consider is the current density used in the welding process. If the current density is too high, it can cause burn-through or other defects in the weld bead. Conversely, if the current density is too low, it can result in an incomplete or weak weld.
In SMAW, defects such as undercutting, slag inclusion, and porosity can occur if the welding technique is not proper or if the electrode is not handled correctly. In FCAW, welding defects such as incomplete fusion and lack of penetration can occur if the welding parameters are not set correctly. In SAW, improper flux coverage or incorrect wire feed rate can lead to welding defects.
To detect welding defects, magnetic particle inspection (MPI) is a commonly used non-destructive testing method. This involves applying a magnetic field to the weld area and then applying a magnetic particle solution to the surface. If there is a defect in the weld, the magnetic particles will cluster around it, making it visible to the inspector.
By selecting the appropriate filler metal, controlling the current density, and using proper welding technique, manufacturers can prevent many welding defects from occurring. In addition, using non-destructive testing methods such as MPI can help detect defects that may have occurred during the welding process. By taking these steps, manufacturers can ensure that their welding processes are producing high-quality and defect-free welds.
Two Broad Categories of Welding Defects
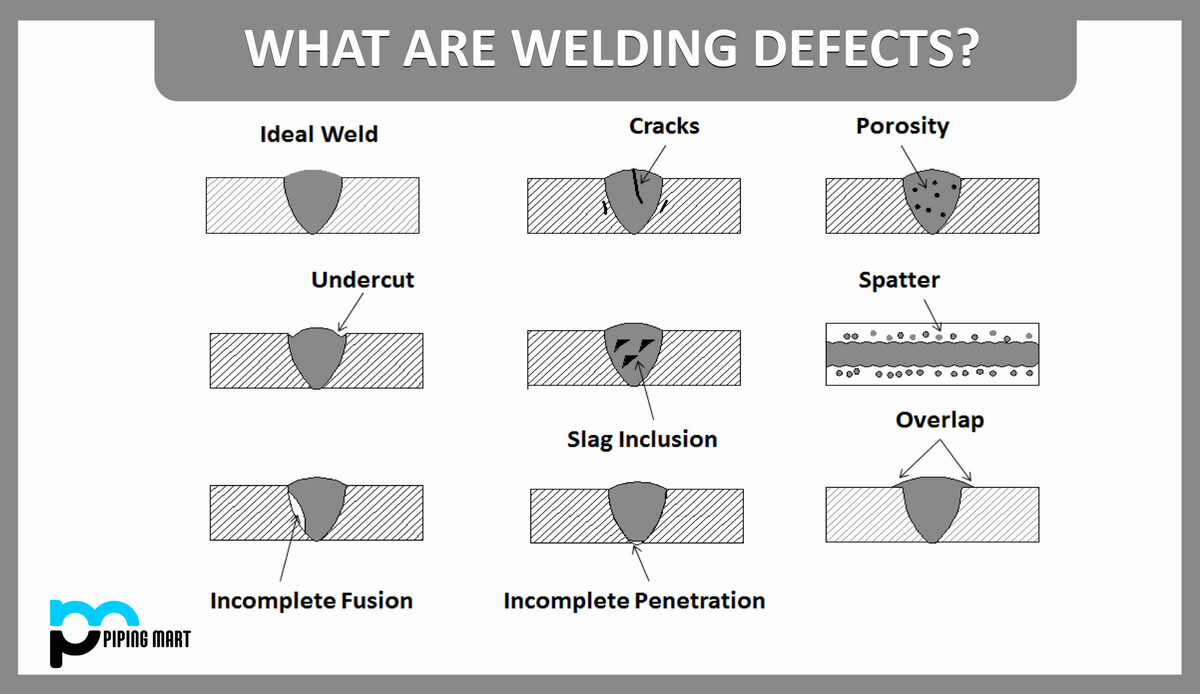
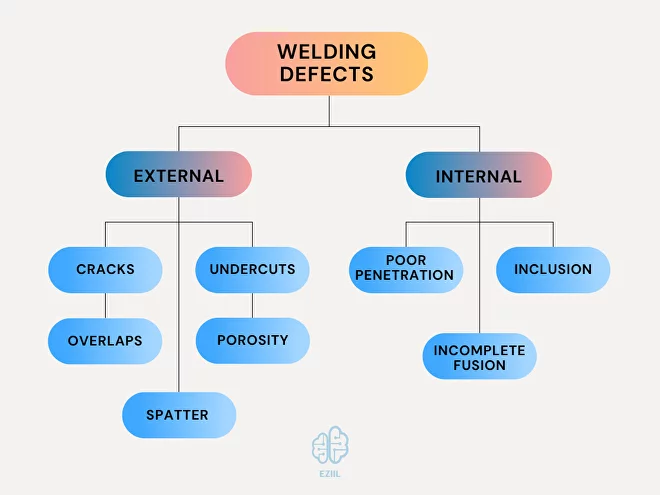
Defects in welding joints can be classified into two categories: defects you can see (external) and those that are hidden (internal).
- External welding defects, sometimes called surface defects, manifest on the weld’s surface. Some examples include cracks, overlaps, undercuts, porosity and spatter.
- Internal welding defects occurring in the depth of the weld might not be visible but are as troublesome as external ones. Included among these are fusion, slag inclusion and incomplete penetration.
Let’s look at these five external defects first:
1. Cracks
Cracks are among the most common and severe defects since they weaken the weld and can occur anywhere on its surface. There are two types of cracks:
- Hot cracks occur during welding when temperatures reach 10,000 degrees Celsius.


View of a hot cracks. These cracks are barely visible to the naked eye.
Image credit: https://weldinganswers.com
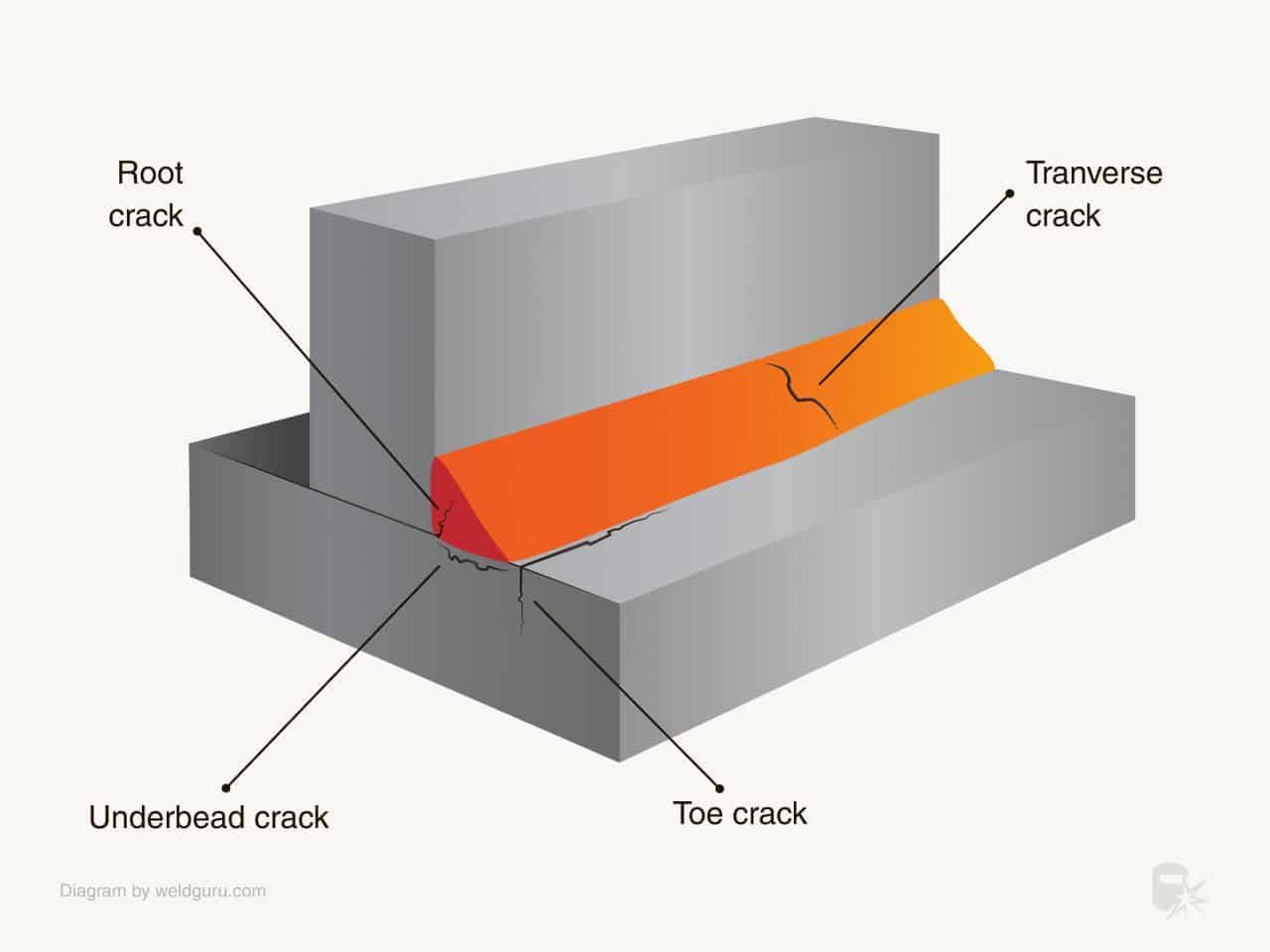
Image credit: https://weldguru.com/welding-cracks/
- Cold Cracks appear after welding and during the solidification process and show up several hours or days after the welding is completed.
Prevention measures for cracks include:
- Avoid rapid cooling of the weld area
- Preheat the joint to the required level
- Avoid low currents coupled with high travel speeds
- Use the correct joint design
- Use proper amperage settings.
- Use the correct alloy filler material

2. Undercuts
Undercuts look like narrow gutters or notches at the edge of the weld. They occur when the base metal melts away from the weld area, reducing the thickness of the base metal and weakening the workpiece.
Prevent undercuts by doing the following:
- Decrease the travel speed
- Use the correct electrode size
- Reduce the length of the arc and lower the voltage
- Use the proper welding techniques
- Do multiple passes
- Keep the torch at the correct angle
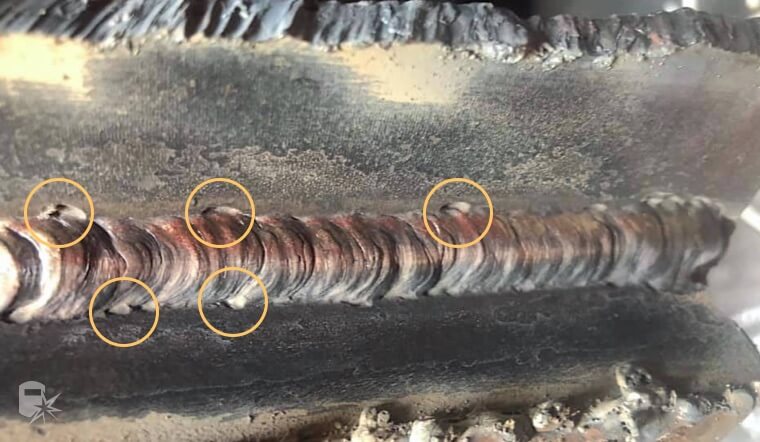
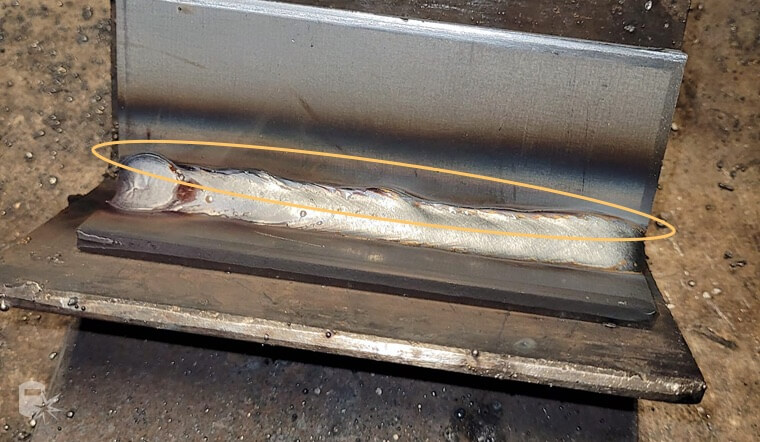


Example of an undercut on the top of the weld.
Image credits: https://weldguru.com
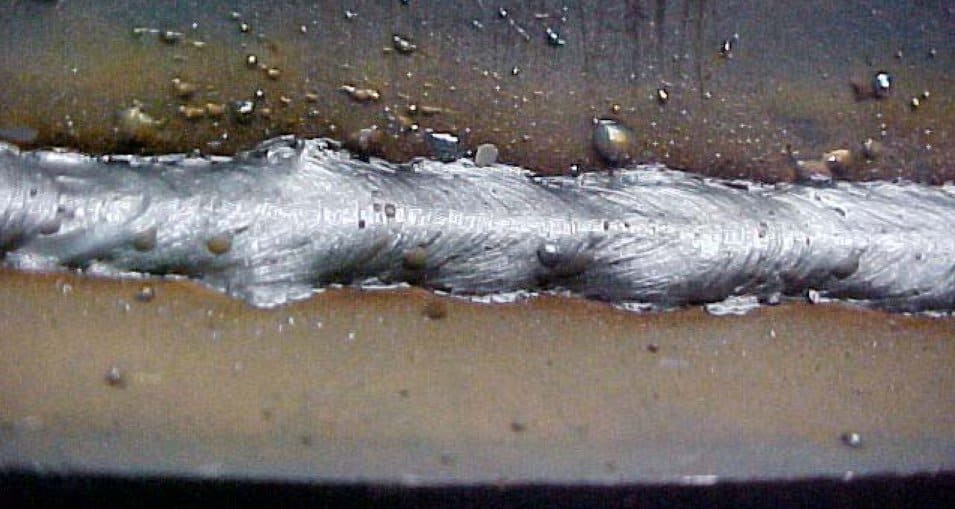

Example of Image credit: https://weldgears.com
3. Overlaps
Overlap results when the weld pool overflows on the surface, covering the base metal without bonding.
Prevention measures for overlap include:
- Use the recommended welding technique to avoid the wrong arc length
- Position the torch at the appropriate angle
- Use the correct deposition
- Use low welding current.
- Avoid letting your travel speed get too slow
- Do not use oversized electrodes
- Set the correct amperage; avoid a high setting

Image credit: https://www.boconline.co.uk
4. Porosity
Porosity occurs when gas bubbles accumulate and get trapped inside a weld. Porous welds typically happen because of contamination of the weld metal. During welding, gases, including steam, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide are generated and can become trapped, weakening the joint and ruining the work.
Consider the following to prevent porous welds:
- Clean the weld surface before you begin welding
- Allow gases to escape by slowing the welding process
- Confirm the settings of the gas flow meter
- Properly clean and prepare the base metal
- Make sure the joint is dry
- Set the shielding gas flow correctly
- Prevent the amperage from getting too high
- Use the correct electrode alloy for the job
Learn more about what is welding porosity.

Image credit: https://www.twi-global.com
5. Spatter
Spatter frequently occurs with MIG welders, and it happens when metal particles from the weld become attached to the surface next to the weld area. Although it’s usually not a threat to structural integrity, spatter is a defect because the aesthetics of a weld are often as critical as the weld’s strength.
MIG welding, a type of welding that uses an electric arc and a wire electrode to melt and join metal pieces, is known to produce spatter frequently.
Reduce spatter with the following suggestions:
- Make sure the base metal is clean
- Use proper gas shielding
- Use the correct amperage
- Keep a short arc
- Increase the electrode angle
- Check the feed wire to ensure it is unimpeded.
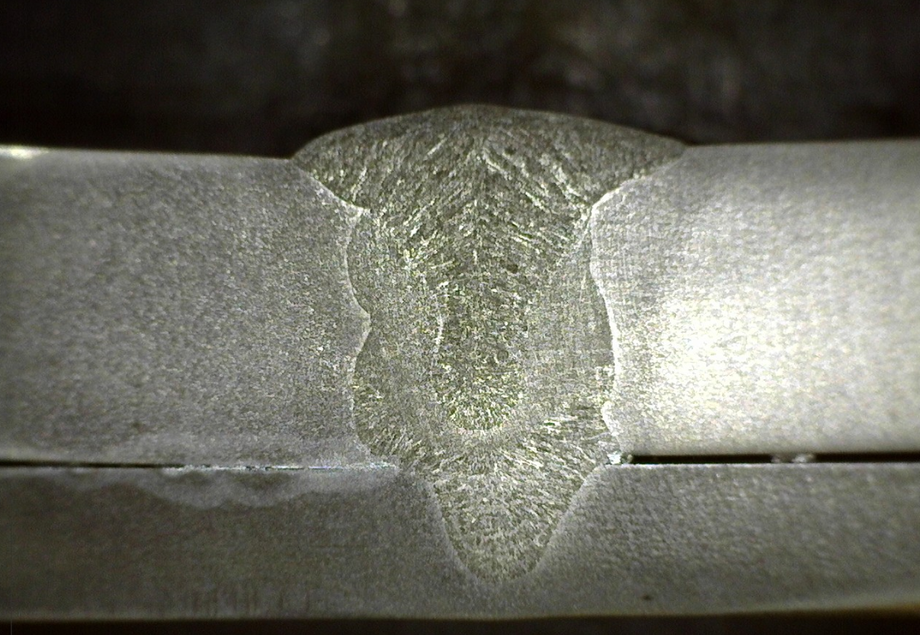

Image credit: https://weldinganswers.com
And here are three examples of internal welding defects:
1. Poor Penetration
Poor or incomplete penetration results when the bead does not fill a butt joint to the bottom, compromising the integrity of the joint.
Prevent incomplete penetration with these welding tips:
- Ensure there is enough weld deposition
- Be sure to use the correct joint geometry and proper alignment
- Use the optimum welding amperage
- Reduce the travel speed
- Use a correctly sized electrode
- Prepare V-grooves for butt joints with 60 to 70-degree sloped sides

Picture credit: https://primeweld.com
2. Inclusion
Slag inclusions are impurities trapped in the weld or on the surface of the weld zone. These contaminants are byproducts of stick welding and arc welding and can significantly weaken the joint.
Prevent inclusions with the following steps:
- Prepare and clean the base metal thoroughly
- Avoid low amperage
- Ensure the weld cools moderately
- Maintain the proper torch angle
- Increase the welding speed so that weld and slag don’t mix

Picture credit: https://www.boconline.co.uk
3. Incomplete Fusion
Lack of fusion (a.k.a. incomplete fusion), occurs when the weld metal and the base metal are not bonded. Incomplete fusion can also occur between layers within the weld itself if the filler material is not well connected to the base metal on both sides and to welds underneath during multiple passes.
Here are a few tips for preventing incomplete fusion:
- Clean the base metal to remove all impurities
- Use the correct size electrode
- Ensure the correct electrode alloy is being used
- Don’t move the torch too fast
- Keep the arc from getting too short
- Keep the amperage high enough
The Darkside of Welding Defects
Welding defects are not merely unsightly but can create serious issues if they are not addressed. In addition to being costly and time-consuming, they could eventually result in injuries or even loss of life if left unchecked.
By learning and using correct welding techniques, professional welders are doing their part to keep themselves and end-users safe in the future. Focusing on improving welding machinery and technical skills helps to limit welding defects and enables manufacturers to produce higher-quality products.