Did you know that there are different types of steel? High strength steels are a specific type of steel with unique properties, benefits, and applications.
In this blog post, we will discuss high-strength steels, their properties, benefits, and applications.
Are you ready to learn more about this versatile material?
Not on EZIIL BOM yet?

Here’s a free online Steel Weight Calculator to help you nail kg/lb fast and avoid over-ordering, surprise freight-class up-charges, and “gotta-grab-a-bigger-forklift” emergencies.
High Strength Steels
Knowledge of a material’s yield strength is very important when designing components, since it usually represents the upper limit of the load that can be applied. Yield strength is very important for controlling many materials’ production techniques, such as forging, rolling or pressing.
HSS is steel with yield strength of more than 250 MPa. As the name implies, high-strength steels offer superior strength and durability.
This makes them ideal for use in a variety of industries, from construction to automotive manufacturing. There are many different types of steel alloys, each with its specific properties and applications.
Benefits of High Strength Steels

High-strength steels are becoming increasingly popular in a wide range of industries. And for a good reason – they offer several advantages over traditional steel.
For one, their higher strength-to-weight ratio allows for lighter, more energy-efficient products. They’re also highly resistant to corrosion and wear, making them ideal for applications where durability is vital.
In addition, high-strength steels can be customized to meet the specific needs of each project, whether it’s increased strength, ductility, or weldability.
As a result, they offer designers and engineers greater flexibility in creating innovative products that meet the challenges of the 21st century.
Available High Strength Structural Steel Types

● Coated – H3
Coated High Strength Structural Steel is a type of steel coated with a zinc layer. This coating helps to protect the steel from corrosion, and it also gives the steel extra strength.
It is often used in the construction of bridges and buildings. It is also used in the manufacturing of cars and trucks. This structural steel is an important part of our modern world and is here to stay.
● Uncoated
Uncoated High Strength Structural Steel is a type of steel that does not have a coating. It is used in the construction of pipelines, and it is also used in the manufacturing of cars and trucks. They are most suitable for use in applications where there is no need for a coating.
● Electro galvanized (EG)
Electro galvanized steel is a type of carbon steel that has been treated with an electrochemical process to create a protective coating of zinc on its surface. EG steel is often used in construction for framing, decking, and other structural applications.
It is also commonly used in the automotive and appliance industries. The zinc coating on EG steel provides extra protection against rust and corrosion, making it an ideal choice for products exposed to harsh weather or other corrosive conditions.
● Hot Dip Galvanized
It differs by the process of coating it. The fabricated steel is dipped into a molten pool of zinc, which is believed to be one of the most effective ways to protect it from rusting when used in embedded soil, concrete, or submerged in water.
Also, for more insights on the composition of galvanized handrails, feel free to explore our article, ‘What Are Galvanized Handrails and Their Uses?‘.
● Hot Dip Galvannealed
For applications involving extreme environments, hot-dipped galvannealed steel is a tough, corrosion-resistant alternative.
It is made by placing galvanized sheet steel into an induction annealing furnace, which causes the iron and zinc layers to disintegrate into one another and form zinc-iron alloys on the surface.
Mechanical Properties of Different
High Strength Steels Types
There are a variety of different high-strength steel types, each with its unique mechanical properties. For example, some steels are particularly resistant to abrasion, while others are more resistant to impact.
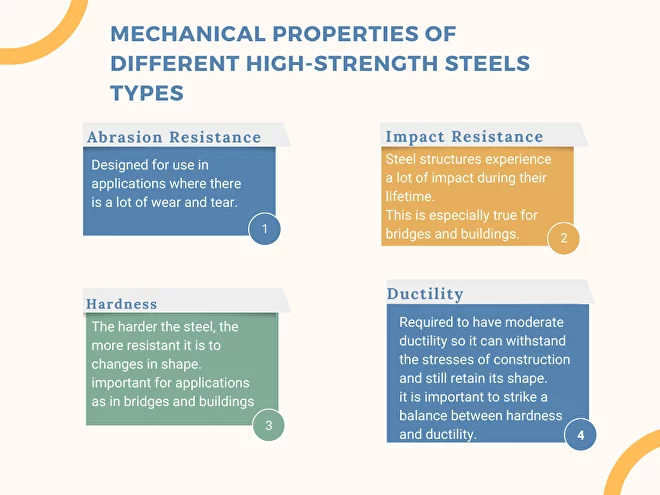
High-Strength Steels Types
● Abrasion Resistance
This property is found in steels that have been designed for use in applications where there is a lot of wear and tear. Structural steels experience a lot of abrasion in their lifetime, so it is vital to choose a steel that can withstand this type of wear.
● Impact Resistance
Steel structures experience a lot of impact during their lifetime. This is especially true for bridges and buildings constantly bombarded by high winds and heavy rain. Choosing steel that can withstand these types of impacts is essential.
● Hardness
Hardness is a measure of a steel’s resistance to deformation. The harder the steel, the more resistant it is to changes in shape. This is important for applications where the steel will be subject to a lot of stress, such as in bridges and buildings.
● Ductility
High-strength steel is required to have moderate ductility so it can withstand the stresses of construction and still retain its shape. High ductility can cause the steel to become brittle, so it is important to strike a balance between hardness and ductility.
Book a 60-minute demo to see
how eziil mrp solution works for you
Applications of High Strength
Low Alloy Steel
High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) steels are a group specifically designed to have higher strengths while maintaining good weldability and ductility.
They are commonly used in the construction industry for applications such as bridge construction, pipeline transportation, and offshore drilling platforms.
However, their use is not limited to large-scale construction projects. HSLA steels can also be used in the fabrication of smaller structures such as storage tanks and containers. Their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them an ideal choice for these applications.
In addition, their resistance to corrosion and abrasion makes them well-suited for use in harsh environments. HSLA steels are a versatile group of steels that can be used in a wide variety of applications including, but not limited to:
● Construction
● Transportation
● Offshore drilling platforms
● Storage tanks and containers


HSLA steels are becoming more commonly used in many industrial applications, including transmission pipelines, shipbuilding, railcars and structural steel.
Picture credits: https://fsmdirect.com/handling-hsla/
High Strength Steel vs. Low Strength Steel
There are many different types of steel, each with its own merits. High-strength steel is often used in construction and engineering applications where its superior strength and durability are required.
On the other hand, low-strength steel is more commonly used in applications where weight is a concern, such as in the automotive industry.
So, which type of steel is right for your application? Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of high-strength and low-strength steel to help you decide.
Strength & Cost
HS steel is much stronger than low-strength steel, making it ideal for applications where load-bearing is required. In addition, HS steel is more expensive than low-strength steel, so it may not be the most cost-effective option for all applications, especially for structural fabrication.
Low-strength steel is less strong and cheaper than high-strength steel, making it a more cost-effective choice for some applications.
However, LS steel may not be suitable for all applications requiring load-bearing.
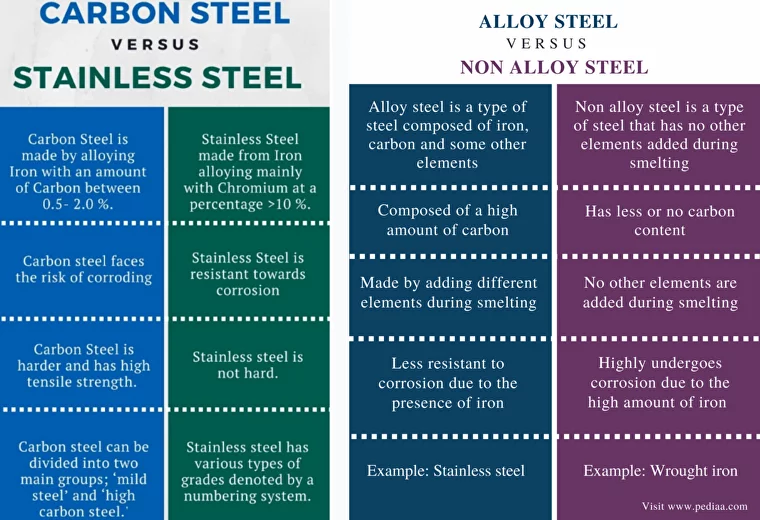
Carbon steel, alloy steel and stainless steel differences.
Photo credits: https://shipbuildingknowledge.wordpress.com and https://euresisjournal.org
Which Steel Grade is Suitable for
Structural Fabrication?
With so many different steel grades on the market, it can be difficult to know which one is best suited for your project.
When it comes to structural fabrication, three main categories of steel are commonly used: Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, and Stainless Steel. Each type of steel has unique properties and benefits that make it ideal for different applications.
Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel is the most commonly used type of steel for structural fabrication. Carbon steel is affordable and provides good strength and durability. However, carbon steel is unsuitable for corrosive environments or high temperatures.
Alloy Steel:
It is a more robust alternative to carbon steel and is often used in applications where strength is critical. However, alloy steel is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more difficult to work with.
Stainless Steel:
It is the most expensive type of steel but has superior corrosion resistance and high temperatures. Stainless steel is often used in food processing and medical applications where hygiene is paramount.
When choosing a type of steel for your project, it is important to consider the environment it will be used and the required strength and durability. Doing so can ensure that you select the best type of steel for your needs.
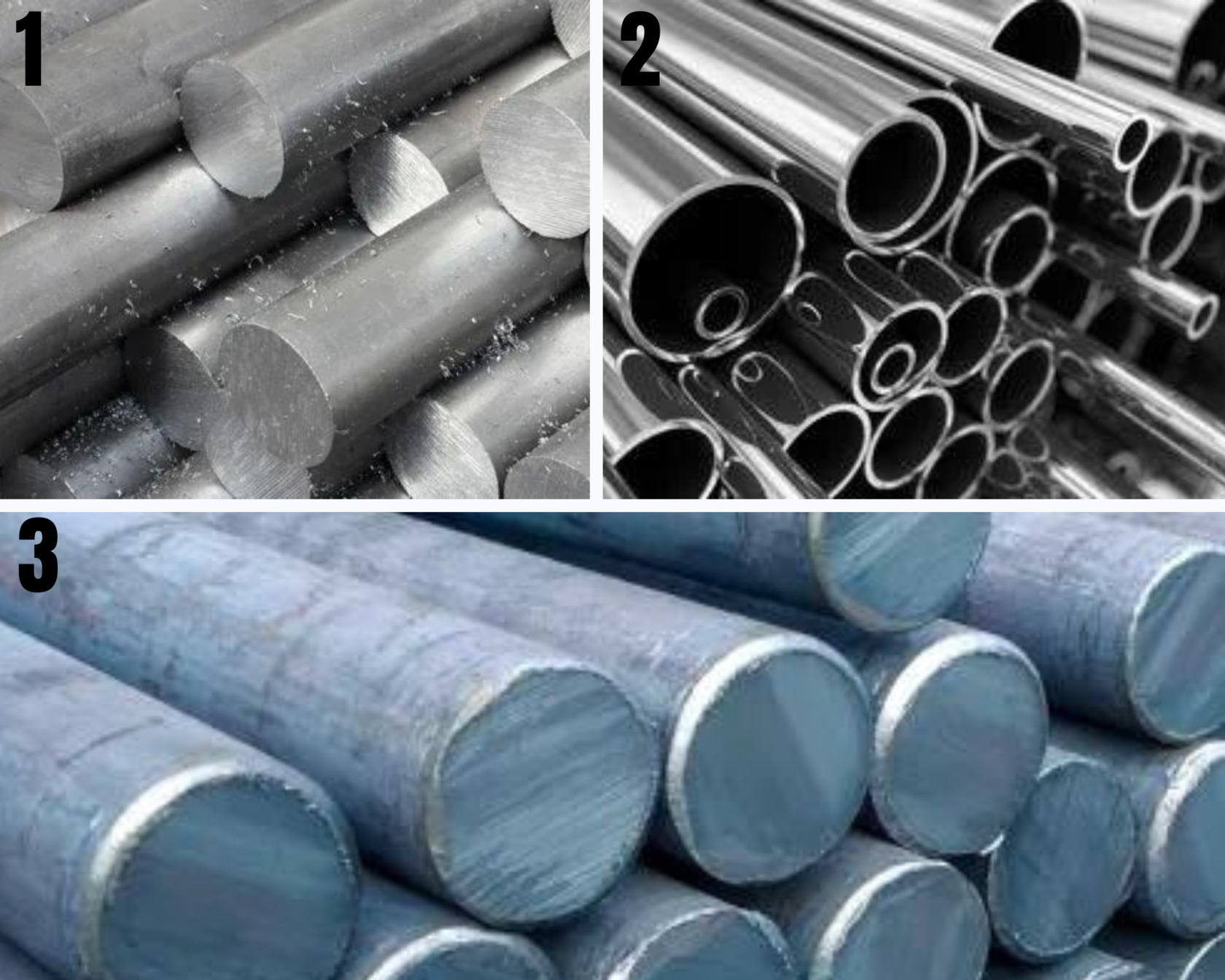

Samples:
1. Alloy Steel
2. Stainless Steel
3. Carbon Steel
Source: https://extrudesign.com
Conclusion
So what are high-strength steels? They are structural steels with a higher strength-to-weight ratio than low-strength steels. This makes them ideal for use in fabricating structures and components that require minimal weight but still need to withstand heavy loads.
Various high-strength steel types are available, each with its unique set of properties. In this article, we’ve looked at the different types of high-strength steels and their mechanical properties.
We’ve also looked at the benefits of using these steels in structural fabrication applications and some of their most common applications.
Finally, we’ve compared high-strength steel to low-strength steel and discussed which type is better suited for specific fabrication needs.
EZIIL is the leading provider of digitalization software for project-based metal fabrication. Our MRP software is designed to help our customers achieve their business goals, and our team is committed to providing the highest level of customer service.