In the beginning, every machine was manually operated. There were no computers, at least not in the machine and fabrication shops. Machinists calculated speeds and feed rates for their milling machines and lathes and controlled their movement using the handles and wheels attached to each axis.
Eventually, over the last several decades, CNC machining evolved from manual machining, where a single machinist or operator was assigned to one machine, to automated machine tools that ran unattended. And the types of CNC machines also increased to cover practically every manufacturing segment.
This article aims to survey the various CNC machines, how they work, and their application. We’ll start with a brief explanation of computer numerical control (CNC) and then list these remarkable machines that have changed and continue to change the face of manufacturing
What is CNC Machining?
Computerized Numerical Control (CNC) is a manufacturing process using computers, software, and codes to control the movements of machine tools, such as milling machines, lathes, and several other types of equipment. CNC machining controls a range of complex machinery, such as grinders, lathes, and turning mills, all of which are used to cut, shape, and create different parts and prototypes. CNC machines are essentially the opposite of “old-school” devices that are manually controlled by hand wheels or levers, or mechanically automated by cams alone.
CNC machines also run faster, have more flexibility, and the components coming from the CNC are typically more accurate. And since these computer-controlled machines are less influenced by human error, repeatability is one of their hallmarks.
Most of the following CNC machines and their systems are integrated with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, making it essential to hire well-trained CNC machinists and programmers to operate the sophisticated machinery.
Overall, CNC machining is a highly versatile and effective manufacturing process that has revolutionized modern industry. Its precision, accuracy, and flexibility make it an essential tool for a wide range of applications, from automotive and aerospace to medical and electronics.
Learn more about how to read CNC blueprint symbols.
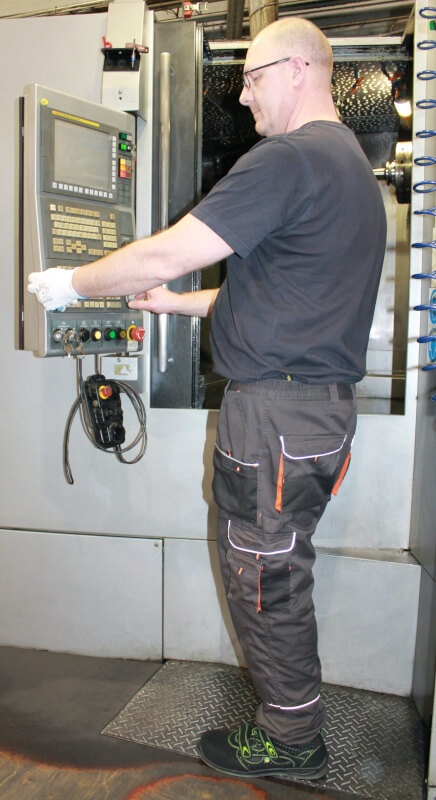
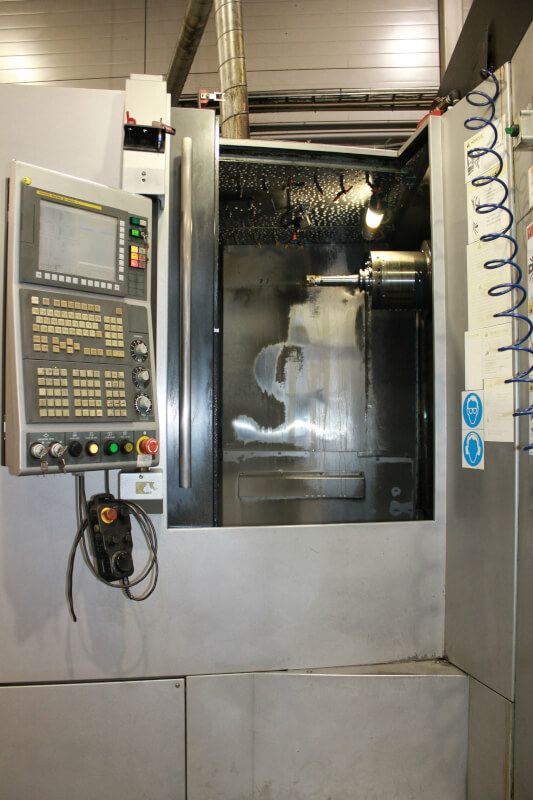
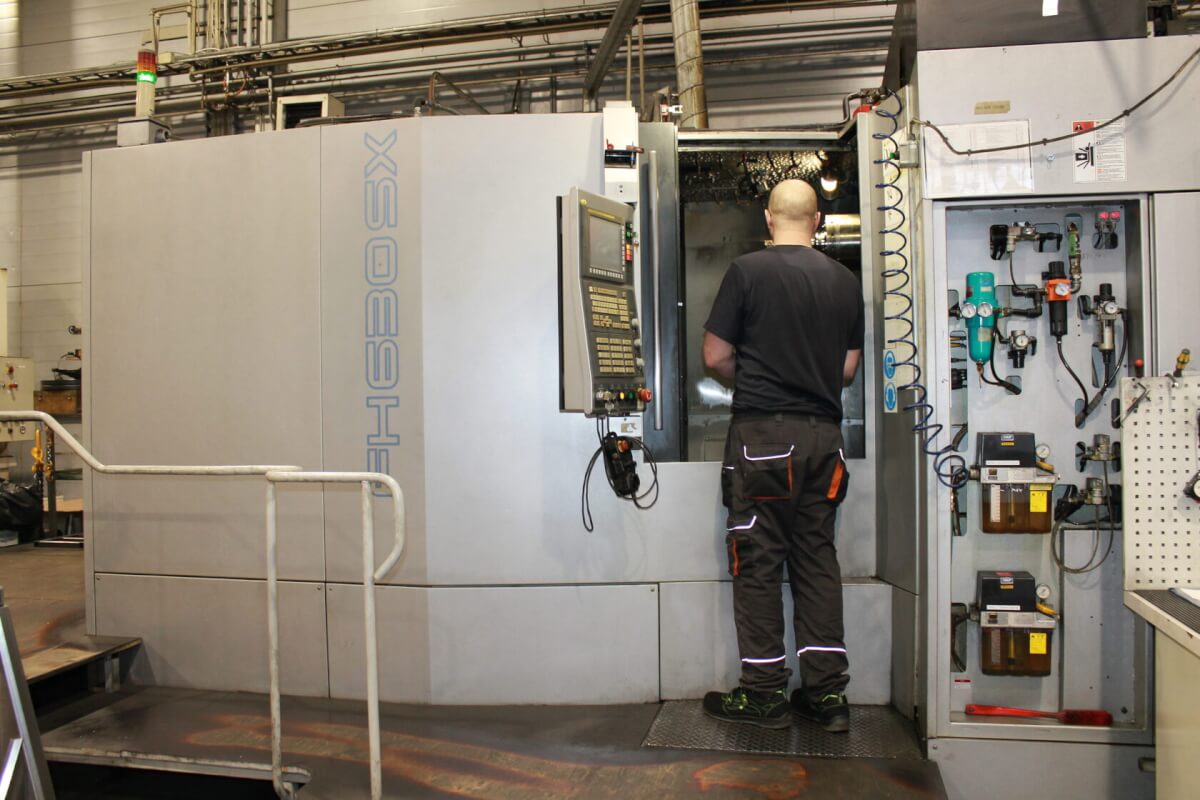
Below you can see some different brands of CNC Machines from Kolmeks AS – they manufacture electromechanical products (for example: elevators and cranes, process and automation, land and marine propulsion with customized motors).
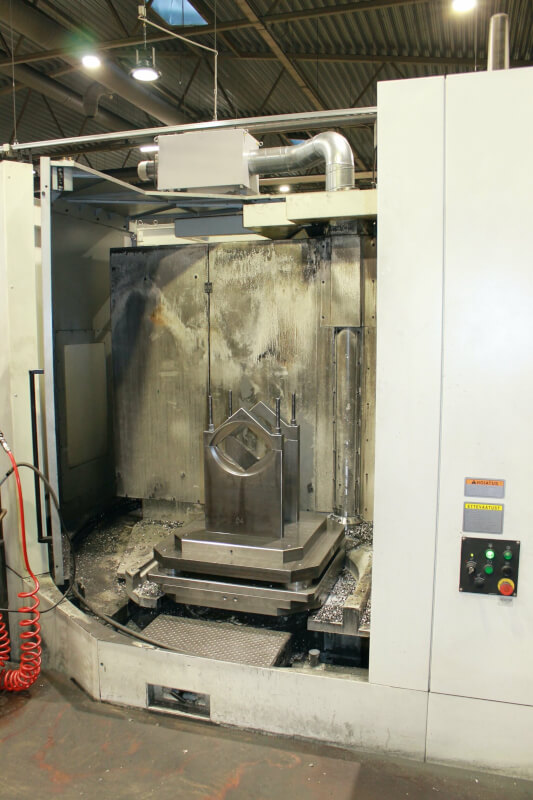
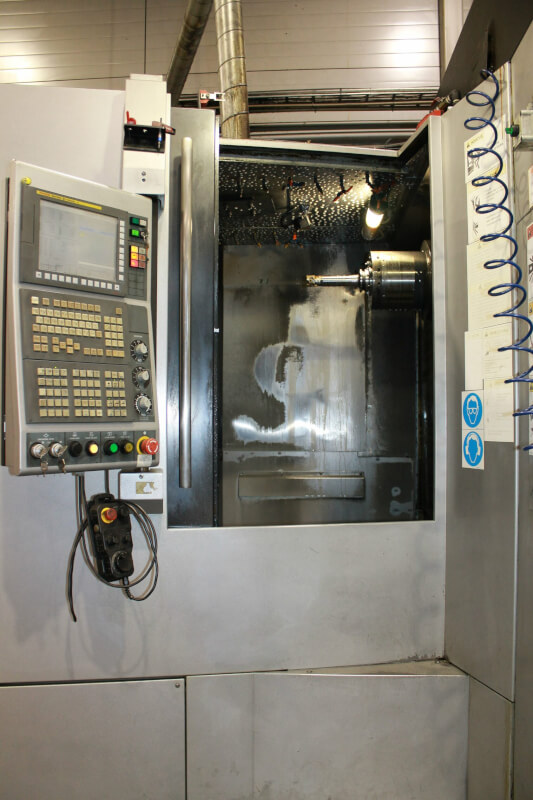
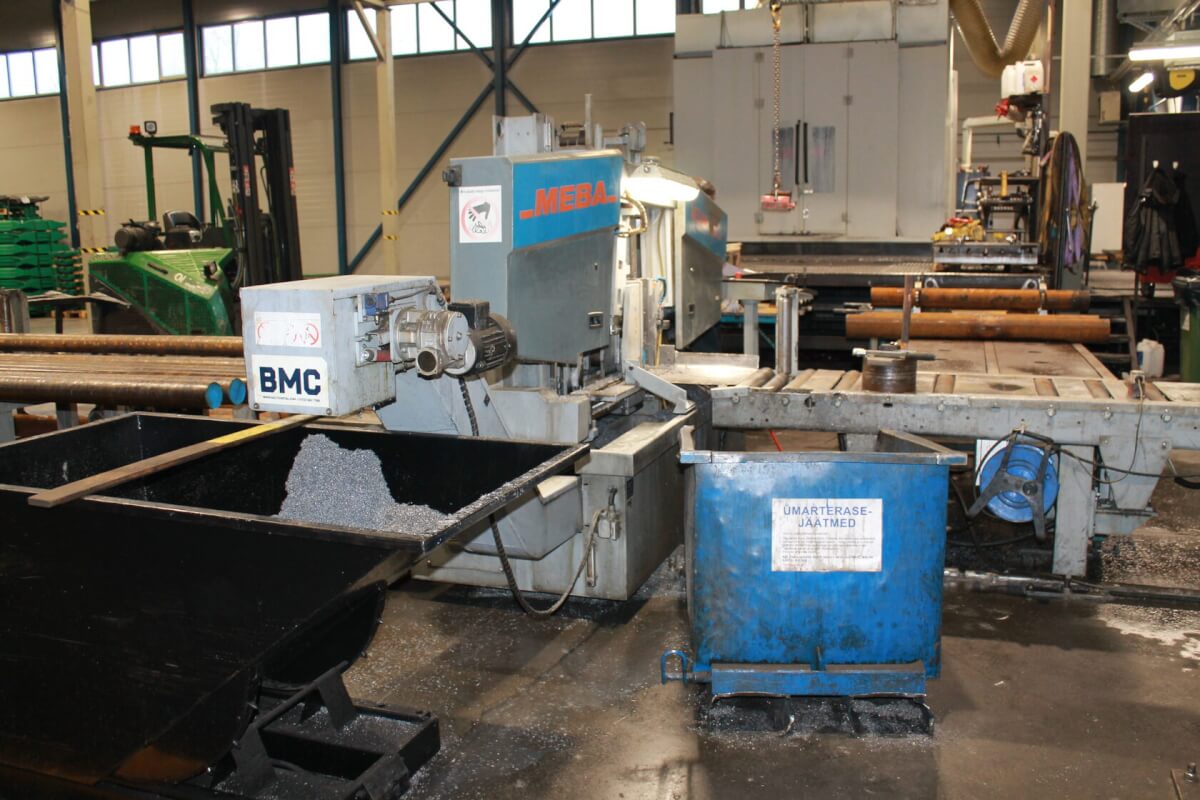



What are the Pros and Cons of CNC?
Although the advantages of CNC machines far outweigh their downside, there are a few things to consider. Let’s start with their positive points:
- CNCs can take on the most complex designs
- They are precise and accurate
- They run much faster than manual machines
- Most of the human error has been eliminated
- CNCs can often run unattended, minimizing labor costs
- They have unfailing repeatability
- Safer to operate because they are typically enclosed
- In most cases, you can skip the prototyping process
- They are versatile
- One operator can sometimes run multiple machines
- Few defective parts
- Lower overall production costs
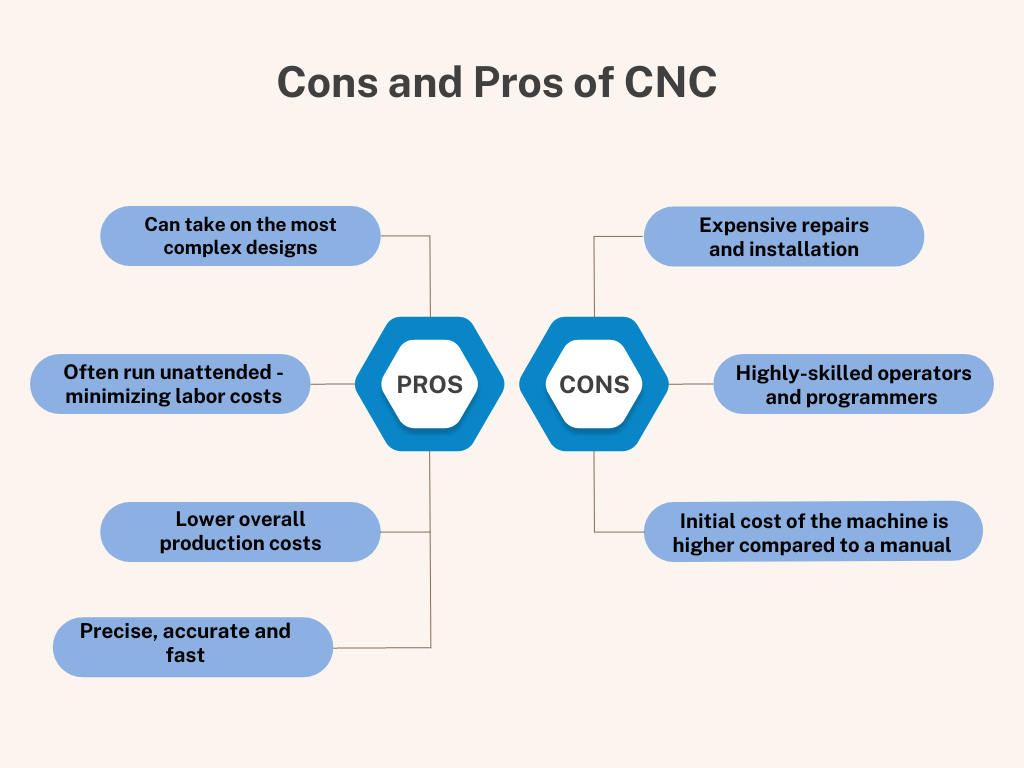
However, they are not without a few negative points:
- The initial cost of the machine is much higher compared to a manual machine
- You will need highly-skilled operators and programmers
- Trained professionals are required to repair breakdowns
- Repairs are expensive
- Installation is costly
Let’s take a closer look at these machines to determine the uniqueness and value in each of them:
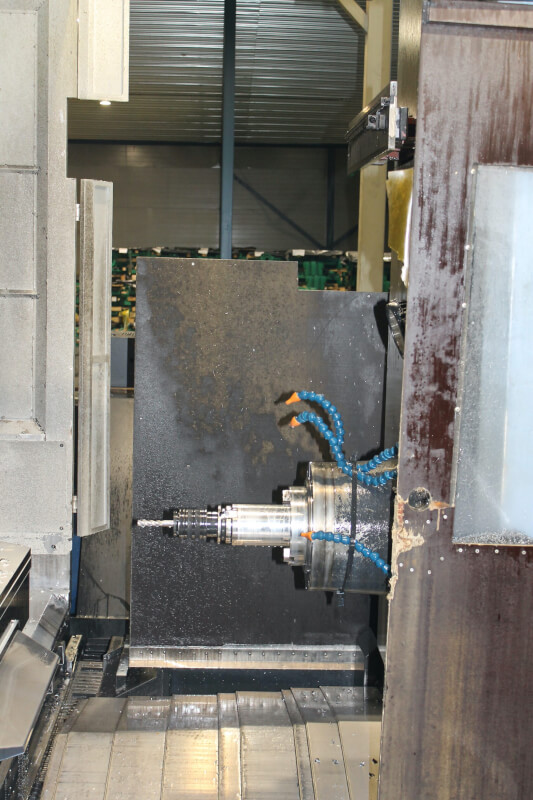
1. CNC Milling Machines
Arguably the most popular CNC machine, the CNC milling machines come in several types, including vertical, horizontal, and multi-axis machining centers. The CNC milling process begins with a design on CAD software, which is later converted into a format for the CNC mill to read.
CAM software exports this to the CNC mill, reads the coded instructions, and puts them into motion, directing each move the machine must make. These moves provide complete machining for diverse parts like cast iron fittings to the most complex components for the military, aerospace, and automotive industries.





2. CNC Lathe Machine
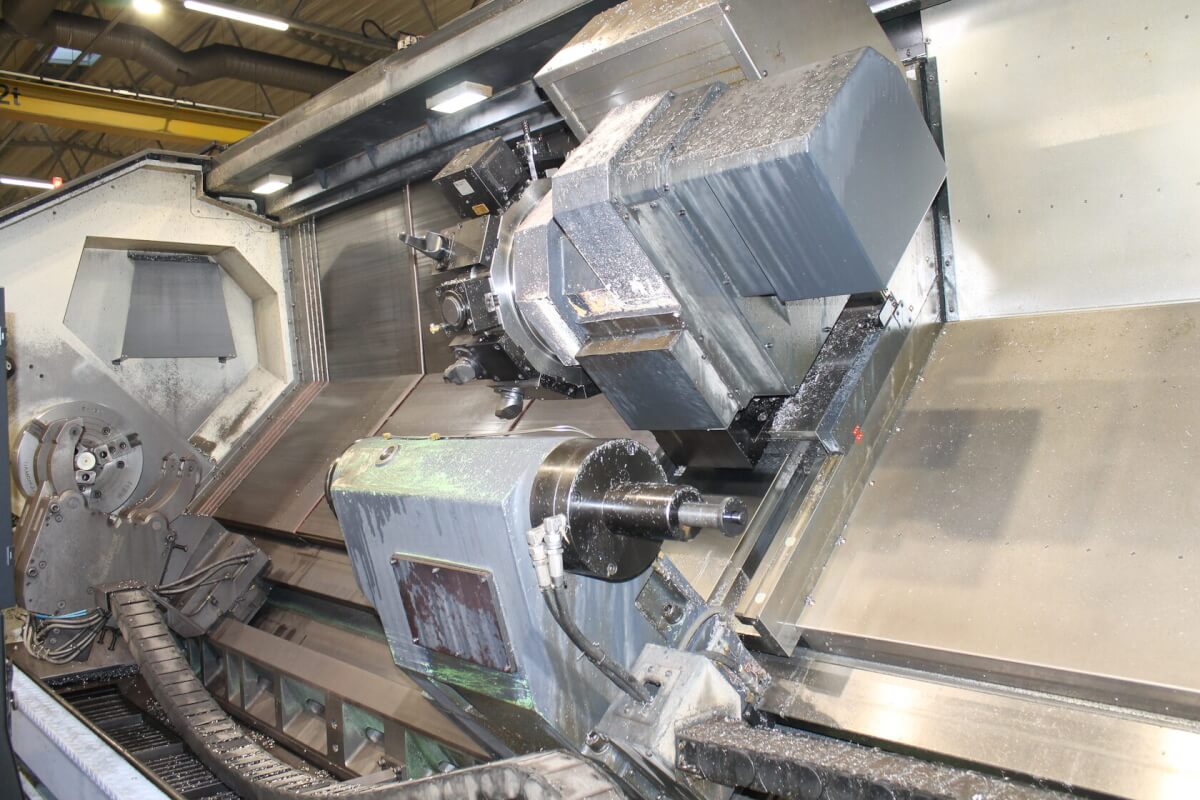
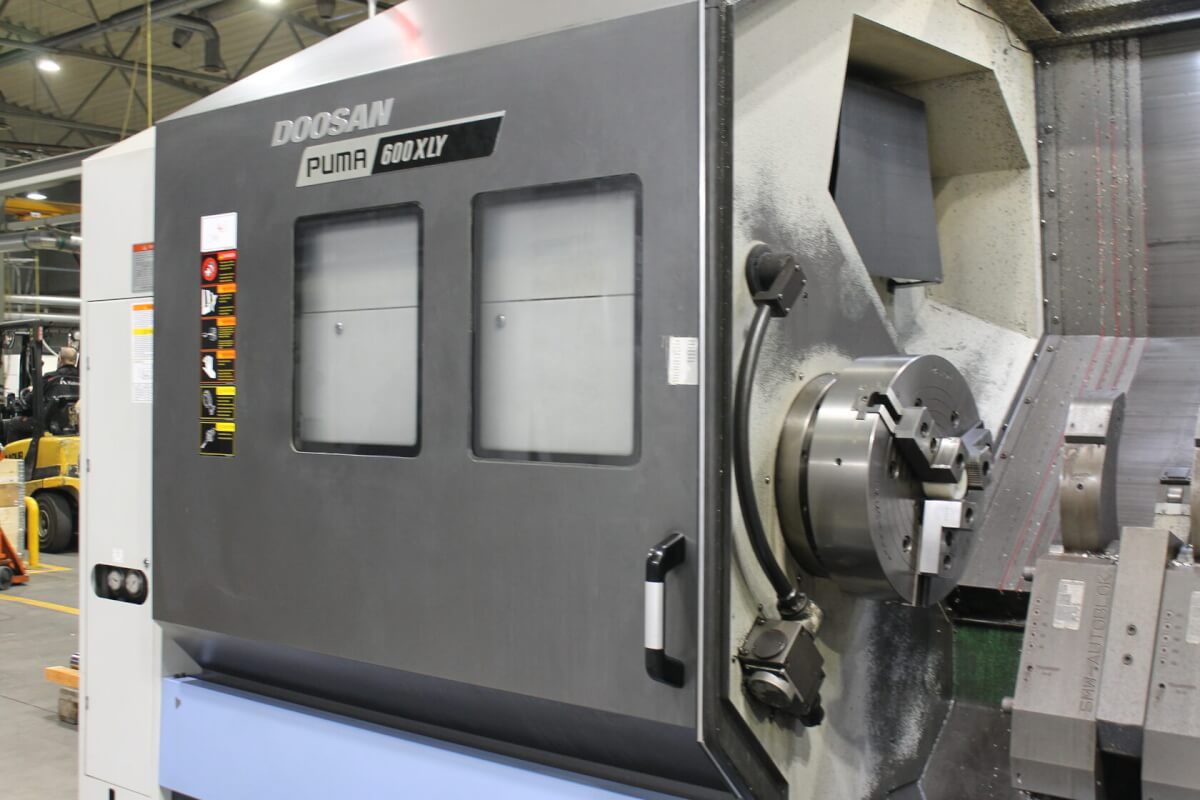
In contrast to the CNC mill, where the cutting tool rotates to remove material from a workpiece, with the lathe, the part being machined spins, and the material is removed using a fixed tool. However, the two machines are similar in that each requires a CAD drawing converted into CAM format for the machine’s tool path.
CNC lathe machines are high-production machines, ideal for producing large quantities of cylindrical-shaped parts quickly and accurately. Other CNC lathes are used for machining parts in a jobbing shop environment or for maintenance work.
CNC lathes are present in almost every industry, including automotive (camshafts), military (gun barrels), furniture (table and chair legs), aerospace, and electronics.



3. CNC Routers
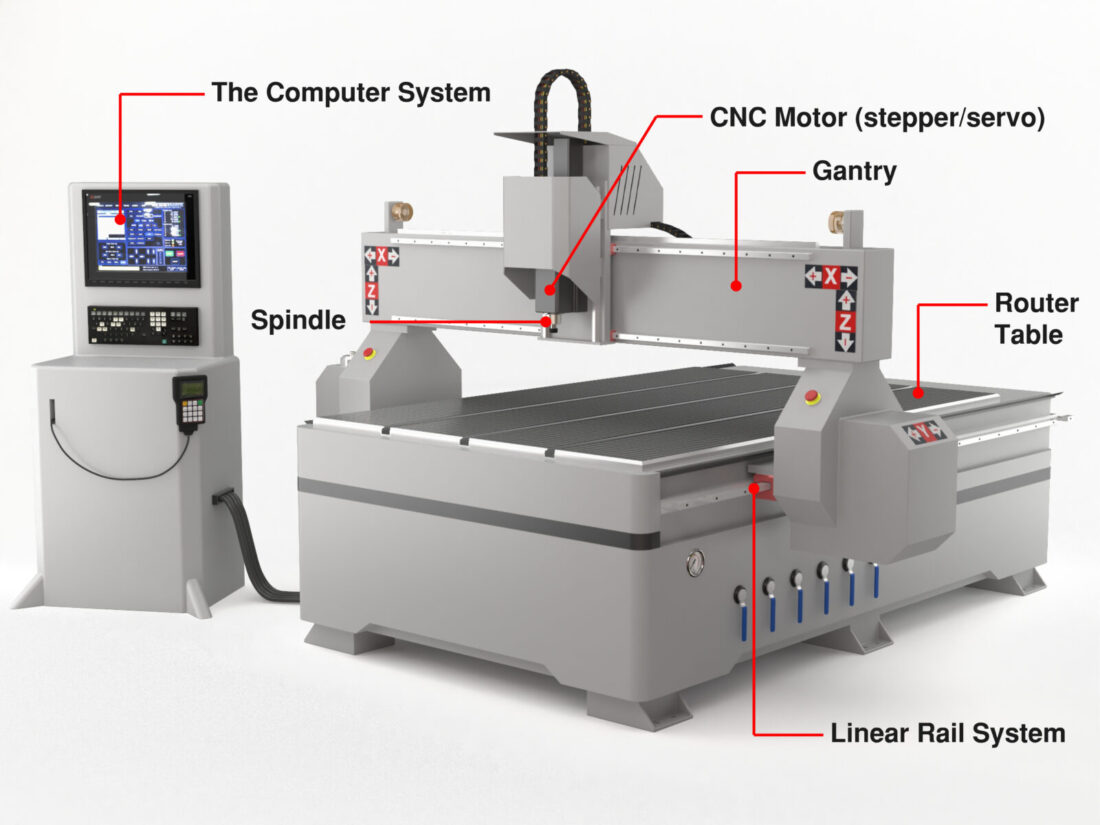
Image credits: https://www.cncmasters.com/
CNC routers work along the same principle as handheld routers, but that’s where the similarity ends. These routers have a large table for the workpiece and move much faster than the handheld. Although they have some of the attributes of a CNC mill, including speed, accuracy, and repeatability, routers will typically work with lighter materials like wood, plastics, aluminum, thin metals, synthetic rubbers, and foam.
As with other types of CNC machines, routers operate with CAM software to create customized three-dimensional parts in manufacturing sectors such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, and HVAC systems. Because routers are among the most straightforward CNC machines to operate, they can save companies on labor costs, produce less waste, and allow workers to work in relative safety.
4. Electrical Discharge Machine (EDM)
EDM machines come in two common types: wire EDM and die-sinking EDM. Although these EDM types contrast in the way they achieve results, they aim to cut shapes that neither CNC mills nor CNC lathes can accomplish, primarily sharp internal corners or deep cavities.
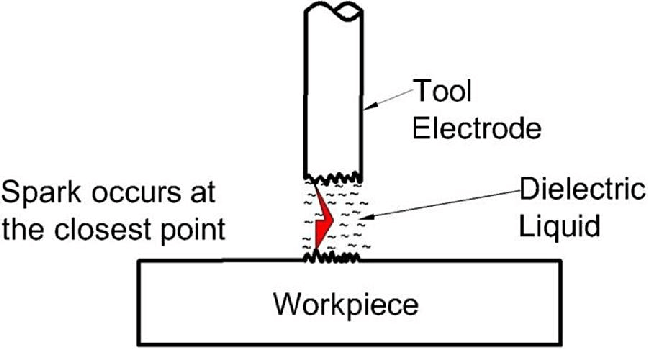
EDM process
Image credits: https://www.researchgate.net
The die-sink process (conventional EDM), often used in mold making, begins with the machine shop producing a graphite electrode in the reverse shape of the cavity. As the electrode is lowered into the workpiece submerged in dialectic fluid, a so-called electric breakdown occurs, and a spark jumps the spark gap. The material vaporizes, and the cavity begins to take shape over time.
Wire EDM produces parts such as extrusion dies, but a very thin electrically-charged wire replaces the graphite electrode to remove the material. A new wire is continuously spooled during the process, avoiding using burnt wire and ensuring accurate cuts. One of the primary advantages of wire over conventional EDM is the elimination of machining a time-consuming electrode.
Image credits: https://www.southshoremanufacturing.com
5. CNC Plasma Cutters
CNC plasma cutting forces a gas or compressed air through a nozzle at high speed. After an electric arc is introduced to the gas, plasma is created and cuts through metal at temperatures of up to 40,000° F. Depending on the material’s thickness, plasma cutters can travel at a feed rate of 500 inches per minute.
The CNC plasma cutting process begins with the creation of a digital design using specialized software, such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing). The design is then uploaded to the CNC machine, which reads the digital file and translates it into instructions for the plasma torch.
CNC plasma cutters can cut through electrically conductive materials, such as steel, aluminum, and brass, often used in automotive repair and restoration shops, fabrication shops, construction, and salvage operations. Plasma-cutting operations are also used extensively in the nuclear industry and for steel buildings, pressure vessels, locomotives, and ships.
One of the main advantages of plasma cutting is its ability to cut through thick materials quickly and accurately. Plasma cutting machines are available in various sizes and power ratings, making them suitable for a range of applications, from small-scale hobbyist projects to large-scale industrial operations.
In conclusion, CNC plasma cutting is a highly efficient and precise cutting process that has become an essential tool in the world of metal fabrication. Its ability to cut through a wide range of metals quickly and accurately, and its ability to create intricate designs and patterns, makes it an ideal choice for a variety of industries. Whether you are cutting thick steel plates or creating intricate metal artwork, CNC plasma cutting is a versatile and powerful tool that can help you get the job done.

CNC plasma cutting systems automate the cutting of intricate shapes in thin materials.
Pictures credit: https://www.fabricatingandmetalworking.com
6. CNC Water Jets
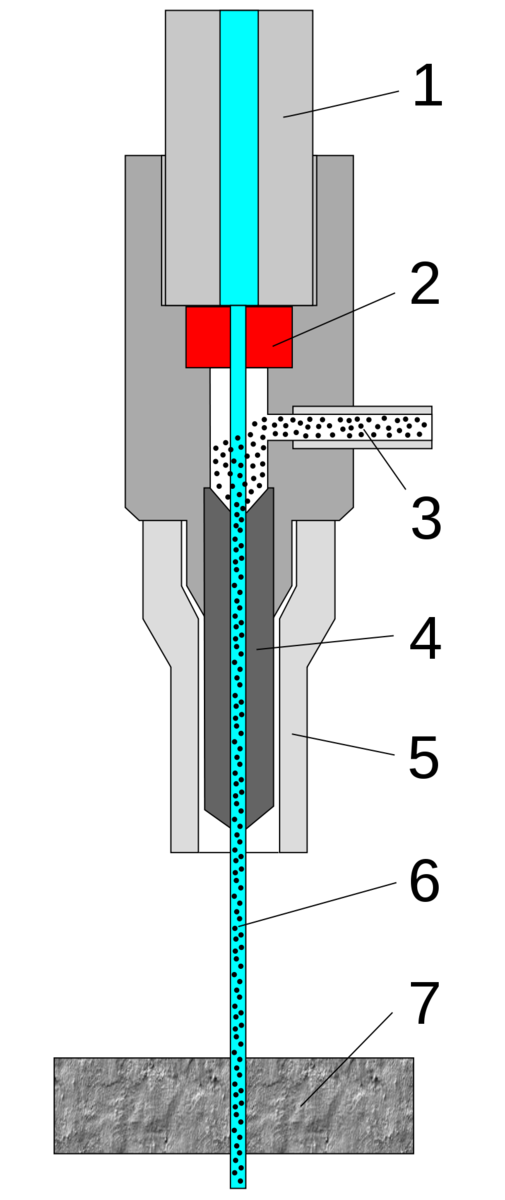
1. high-pressure water inlet
2. jewel (ruby or diamond)
3. abrasive (garnet)
4. mixing tube
5. guard
6. cutting water jet
7. cut material
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org
As the name suggests, a CNC water jet uses the power of high-pressure water to cut various materials. Water alone is enough to cut softer materials such as wood and rubber. Still, an abrasive substance, such as aluminum oxide or garnet, is added when cutting harder materials like steel.
Water pressure of up to 60,000 PSI is forced through a nozzle opening of around .010″ to .015″ in diameter during the cutting process. To reduce the noise and mess, the cutting is completed underwater.
One of the advantages of using a water jet is the lack of heat applied to the material, meaning there are no “heat affected zones” and no interference with the material’s structure as when high heat is applied using other methods. Water jet manufacturers believe their CNC machine could replace gear cutting, profile milling, broaching, and slitting in industries as diverse as aerospace, automotive, and mining.
7. CNC Laser Cutters
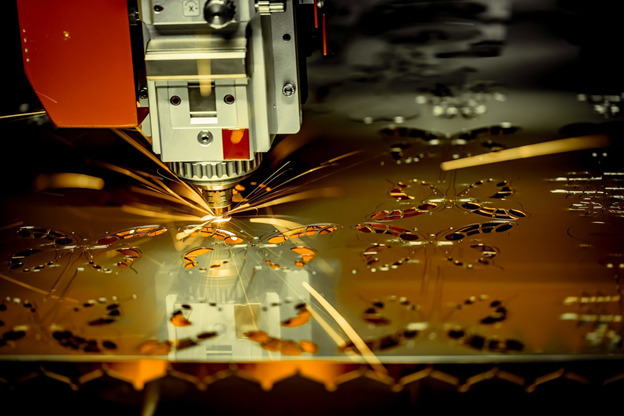

Image credit: https://www.thomasnet.com
Cutting designs into a metal sheet.
Image credit: https://www.thomasnet.com
CNC Laser Cutting Machines: These machines use a laser beam to cut through sheet metal. Laser cutting is ideal for precise cuts and intricate designs, making it a popular choice for high-precision sheet metal fabrication.
CNC laser cutting involves using a focused, high-powered laser beam to remove material. Laser cutters can engrave parts or cut them to create custom parts. Although a CNC laser cutter uses G-code to perform these cutting actions, they use a different method than most other CNC machines.
Using a non-contact, thermal-based process, a CNC laser cutter has a laser head that focuses a column of high-intensity light on a workpiece, melting and cutting the material to the correct shape. Laser cutters are fast, accurate, and capable of creating intricate designs while eliminating the need for cutting tools and generating less waste.
Because laser cutting is a non-contact process, material contamination and distortion risk is reduced, making it a preferred machining method in the medical industry.
Laser engraving is a process that uses a high-powered laser to etch or engrave designs or patterns onto a wide variety of materials, including wood, metal, glass, and plastic. The laser beam is focused through a lens and directed onto the material, which is then melted or vaporized to create the desired pattern.
CNC machines have revolutionized the laser engraving process by automating the entire process, from the design to the engraving. This allows for a high level of precision and accuracy, resulting in crisp, detailed engravings.
Book a 60-minute demo to see
how eziil mrp solution works for you
8. Multi-Axis Machining Centers
While conventional milling machines offer three axes (X, Y, and Z), multi-axis machine tools allow motion in four or more directions, enabling them to produce some of the most highly complex components imaginable.
Multi-axis machines provide enhanced manufacturing flexibility and closer tolerances by allowing the machining of several part sections with one machine setup. Suitable for various industries, these machines are faster, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity.
Greater accuracy, precision, and repeatability are all but ensured with one of these machines. However, a word of caution is in order since these machines can give a severe case of sticker shock as prices reaching several hundreds of thousands of dollars are the norm.
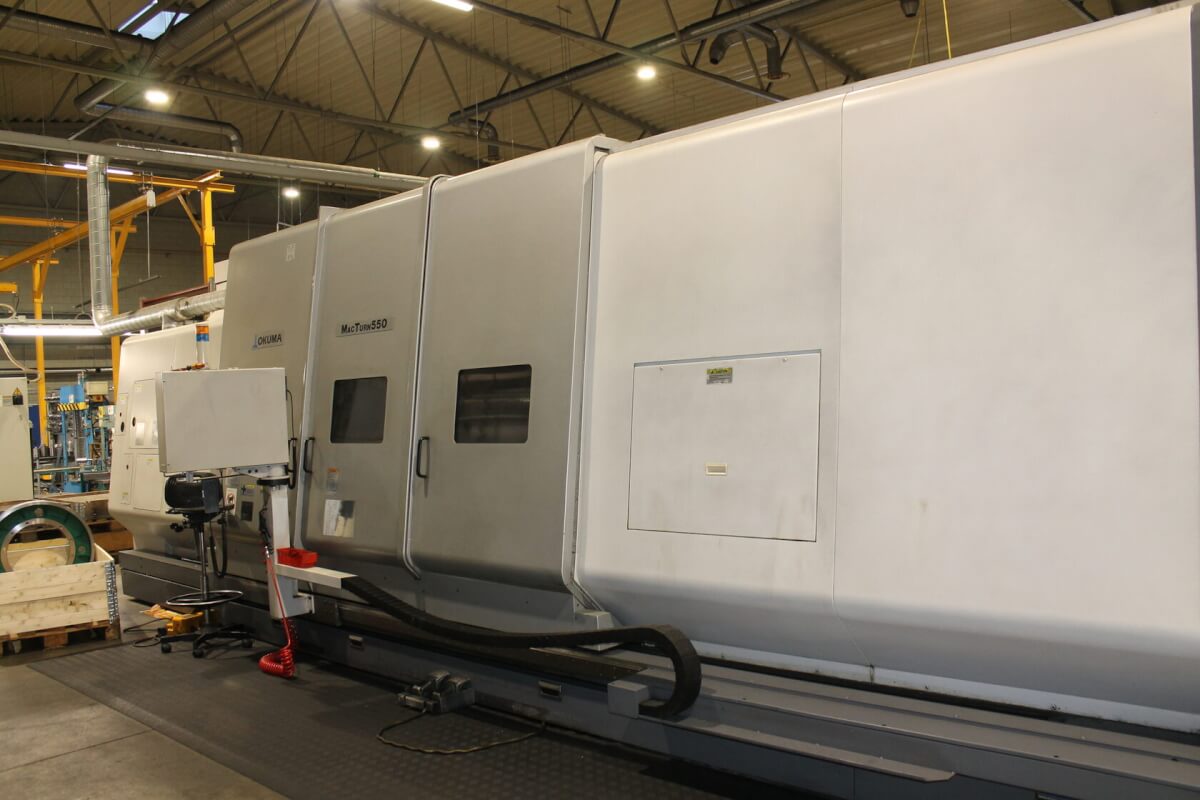
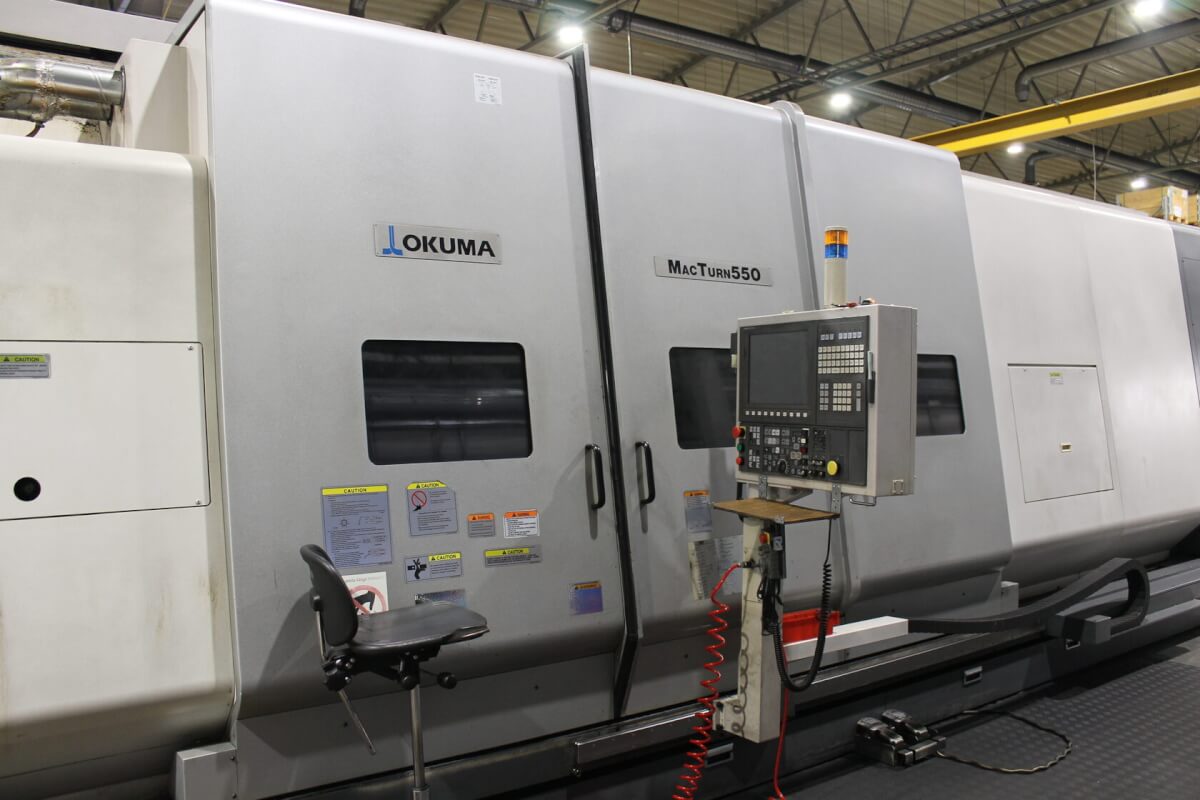


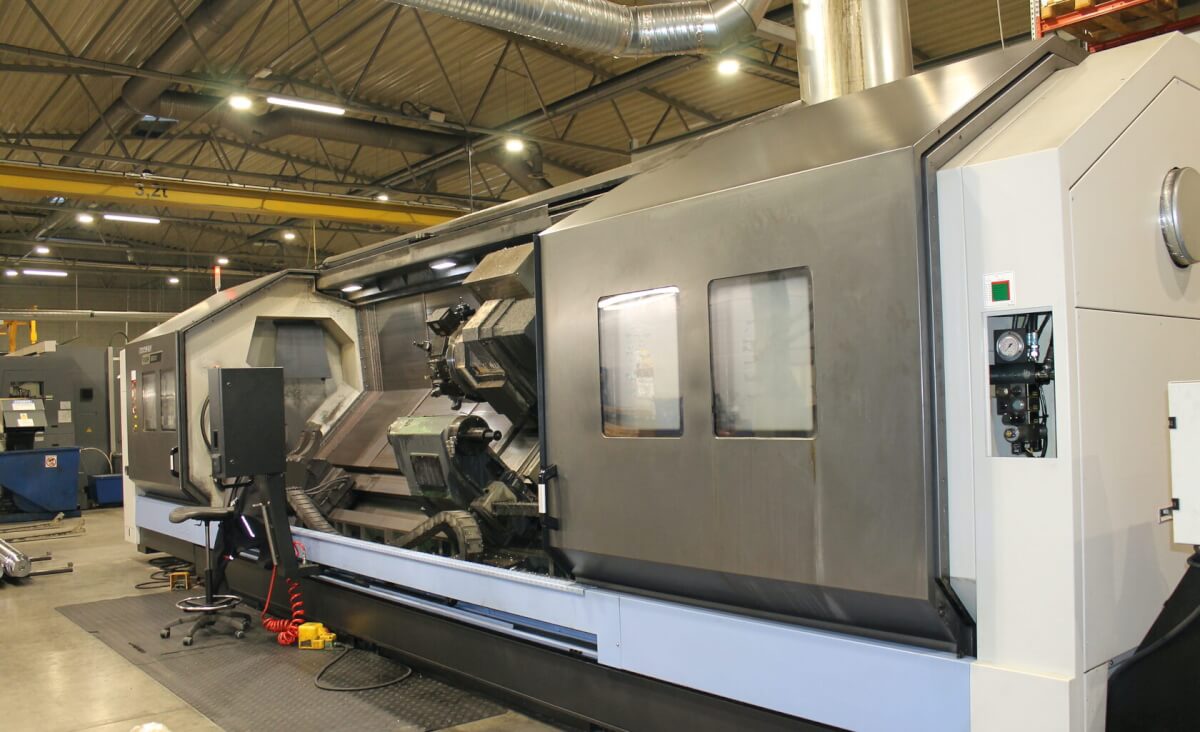
Multi-Axis Machining Center at Kolmeks AS
Okuma MACTURN 550
9. 3D Printers
Each of the previous machines is part of subtractive manufacturing. In other words, they remove material to get the desired shape. 3D printers are the relatively new kids on the block and bring with them a unique method for producing objects: additive manufacturing.
With 3D printing, the machine lays down successive
layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers becomes a
thinly sliced cross-section of the object. As with other CNC machines,
everything begins with a 3D model, and many software tools help you build the
object.
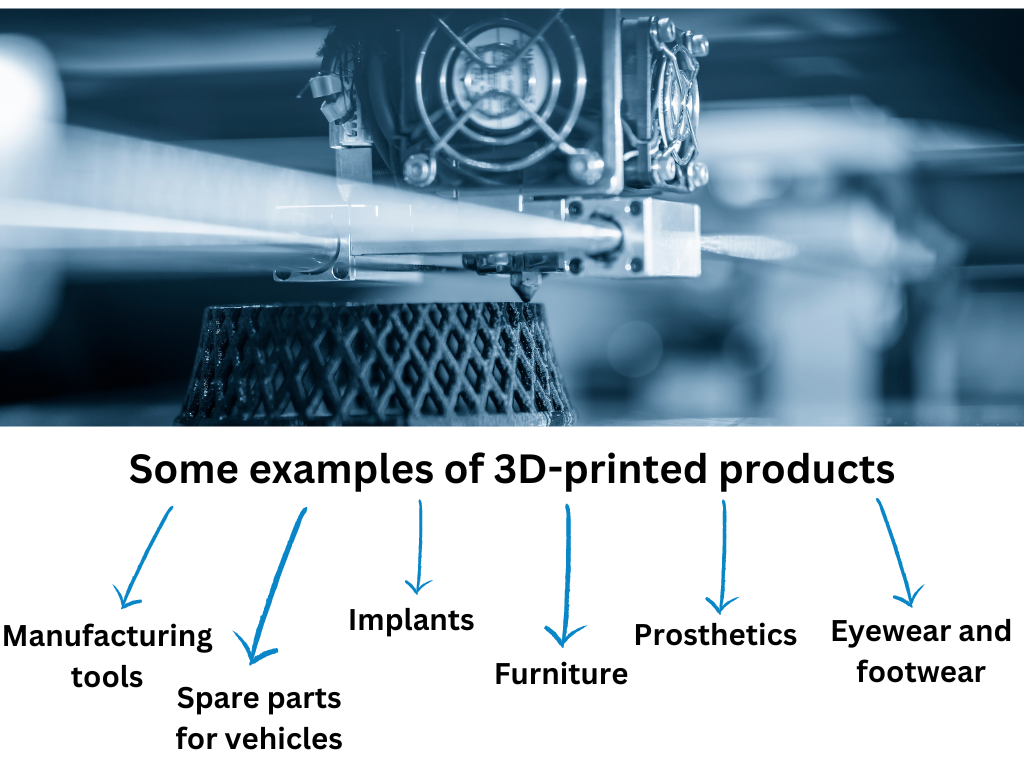
Once strictly used for prototyping and producing one-off orders, 3D quickly became part of production technology. Some examples of 3D-printed products include:
- Eyewear and footwear
- Prosthetics
- Manufacturing tools
- Furniture
- Spare parts for vehicles
- Implants such as hip replacements
Conclusion
CNC machines have become ubiquitous since they are now within the financial reach of even the smallest manufacturing companies. And businesses not joining the march to CNC technology are falling farther behind their competitors.
Manual milling machines, lathes, and drill presses that once ruled the machine shop are now mostly idle as backups to their computer-driven replacements. And for a good reason: they are more efficient, run faster, perform consistently, produce quality components, and have a stellar safety record.
For those who wish for the simplicity of the good old days, you’re already working in them!