Do you want to manage your manufacturing process and resources effectively? Consider using Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. Understanding MRP vs ERP can help you optimize your workflow, ensuring you have the necessary materials on hand when you need them. These systems also assist in tracking inventory levels and budget constraints. This blog post will discuss the benefits of MRP and ERP systems software for manufacturers. Let’s get started!
What is MRP? What is MRP stand for?
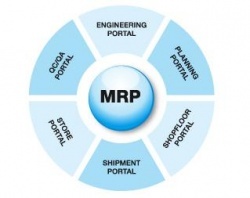
MRP is a software system that helps manufacturers manage the production process by planning the necessary materials and resources required to complete a project. MRP systems are designed to streamline production and minimize waste. Additionally, MRP systems can help manufacturers track inventory levels and capacity constraints.
Key features
There are a variety of MRP software systems available on the market today. Some of the key features and benefits of MRP software include:
- Improved production planning: MRP software can help you more effectively plan your production process, ensuring that you have the necessary materials and capacity on hand when you need them.
- Reduced lead times: MRP software can help you reduce the lead time for your projects, making your manufacturing process more efficient by better planning and information flow.
- Decreased costs: MRP software can help you reduce waste like production stops and other type of noncompliences. This will increase efficiency, resulting in lower production costs.
- Improved customer satisfaction: MRP software can help you better manage your production process, resulting in improved customer satisfaction that come from competitive price, quality and delivery time.
Working on an MRP Software
MRP systems are designed to streamline the production process by planning the necessary materials and resources required to complete a production project. These systems are typically used with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
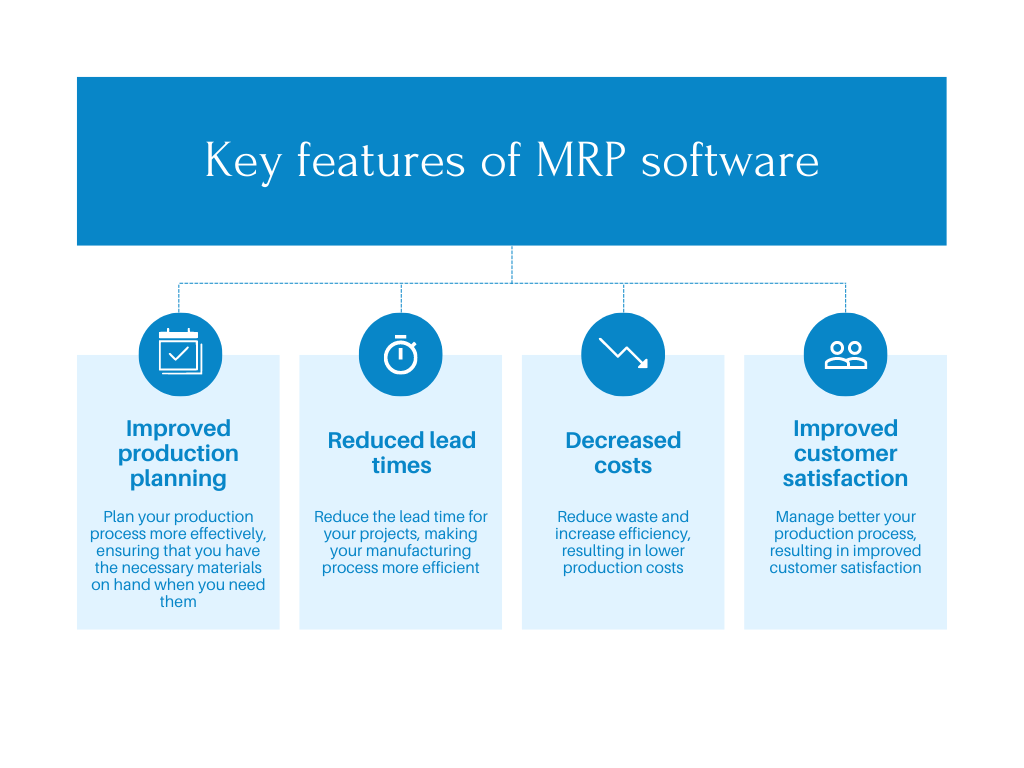
MRP system is composed of four main components:
- The Bill of Materials: The BOM is a list of all the materials and components required to produce a product. It includes information such as the parts, descriptions, and quantities of the materials and components needed. Also drawings and in some cases also production roating. Learn more how to make a BOM!
- The Master Production Schedule: The master production schedule (MPS) is a plan that outlines the production schedule. The MPS includes information such as the types and quantities of products to be produced, the resources required to produce those products, and the order in which the products will be produced.
- The inventory records: Inventory records are used to track the levels of materials and components on hand. These records include stock levels, safety stock levels, and reorder points.
- Shopfloor control: work tasks from master production schedule will get to a shop floor so worker can see in workstation what he needs to do and in what order. Giving back also feedback what is started, what is done, how much and also about noncompliances.
MRP system uses these four components to generate a production schedule. The production schedule is then used to create purchase orders for the necessary materials and components. Additionally, MRP systems can generate reports showing the production process’s status. These reports can be used to identify bottlenecks and improve the production process.
There are a variety of MRP software systems available on the market today.
History of MRP, MRP I, and MRP II
The history of MRP systems dates back to the early days of manufacturing. Joseph Orlicky developed the first MRP system in the 1950s. Orlicky’s system was designed to help manufacturers plan the production of military equipment. The first MRP system was manual and used a card-based system to track inventory levels and production schedules.
The MRP 1 system was developed in the 1960s to address the challenge of managing inventory levels for individual components in a manufacturing process. The system was designed to track the specific materials needed for each product and generate production schedules that would minimize the risk of overstocking or running out of supplies. MRP 1 was quickly adopted by companies across various industries, becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
In the 1980s, the MRP system evolved into the MRP II system. This system is computer-based and uses sophisticated algorithms to generate production schedules. Additionally, MRP II systems include tools for managing quality, capacity, and inventory. They are operated by various industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Benefits and limitations of MRP
There are several benefits to using MRP systems. It can help optimize your production process by reducing inventories, increasing efficiency, and improving customer satisfaction. Additionally, MRP systems can provide a complete view of your production process and help you identify bottlenecks.
However, these systems have some limitations. One of the most significant limitations is that MRP systems require a large amount of data to be entered into the system. This data can be challenging to collect and manage. Additionally, this system can be complex and expensive to implement.
What is ERP?
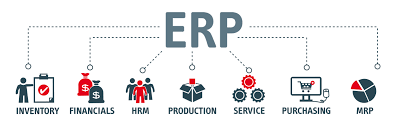
ERP (Enterprise resource planning) software helps organizations manage their business processes. ERP software is used by various organizations, including manufacturing, distribution, and service companies. It includes a variety of modules, such as accounting, human resources, customer relationship management, and supply chain management.
Key features
ERP software typically includes the following features:
- Financial management: It can help you manage your financial processes, such as invoicing, accounting, and budgeting.
- Human resources management: The software can help you manage your human resources processes, such as employee tracking, payroll, and benefits.
- Customer relationship management can help you manage your customer relationships, such as sales and marketing.
- Supply chain management: ERP software can help you manage your supply chains, such as inventory management, order tracking, and supplier management.
- ERP can also help you track production processes, such as material requirements and capacity planning. This is part that can be done also by the MRP software.
Depending on the organization’s needs, ERP systems can vary in size and complexity. It can be implemented as on-premise software or as cloud-based software.
An ERP system typically consists of a database and user interfaces. The database is used to store data related to the system, whereas the user interfaces provide a way for users to interact with the system. The database includes the list of parts and their SKU-s.
These systems can be implemented as on-premise software or as cloud-based software.

History
ERP systems were first developed in the 1960s when manufacturers began to use computer systems to track inventory levels. They were initially designed to help organizations manage their manufacturing processes. Later they were expanded to include other business processes, such as financial, human resources, and customer relationship management. ERP systems are now used by various organizations, including manufacturing, distribution, and service companies.
Book a 60-minute demo to see
how eziil mrp solution works for you
Benefits
- It can help organizations automate their business processes.
- It can also help organizations track their production process.
- ERP can help organizations improve their financial, human resources, customer relationships, and supply chain management processes.
- It can also help organizations reduce their costs.
- ERP software can help organizations increase their revenues and improve customer service.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software also plays a vital role in improving their decision-making and efficiency.
- The software can also help organizations improve their competitive advantage. Moreover, ERP software also assists in enhancing the organization’s shareholder value, attracting and retaining employees, improving compliance with government regulations, managing risk, and improving environmental performance.
Limitations of ERP software
- ERP systems can be complex and expensive to implement as they are difficult to customize. They can be disruptive to businesses due to inflexibility at a certain level.
- The software can be resource-intensive as they require a significant amount of training for users.
- It can have a negative impact on business performance if not implemented properly and are difficult to upgrade.
- ERP software can be challenging to integrate with other software systems.
Relationship between ERP and MRP – MRP vs ERP Software Systems
You must be wondering what is MRP/ERP systems, what MRP is in business. ERP systems typically include MRP functionalitys. In some cases it’s not enough or is not specific to industry it is used. In this cases companies use specific MRP to control production and integrate financial side with existing ERP.
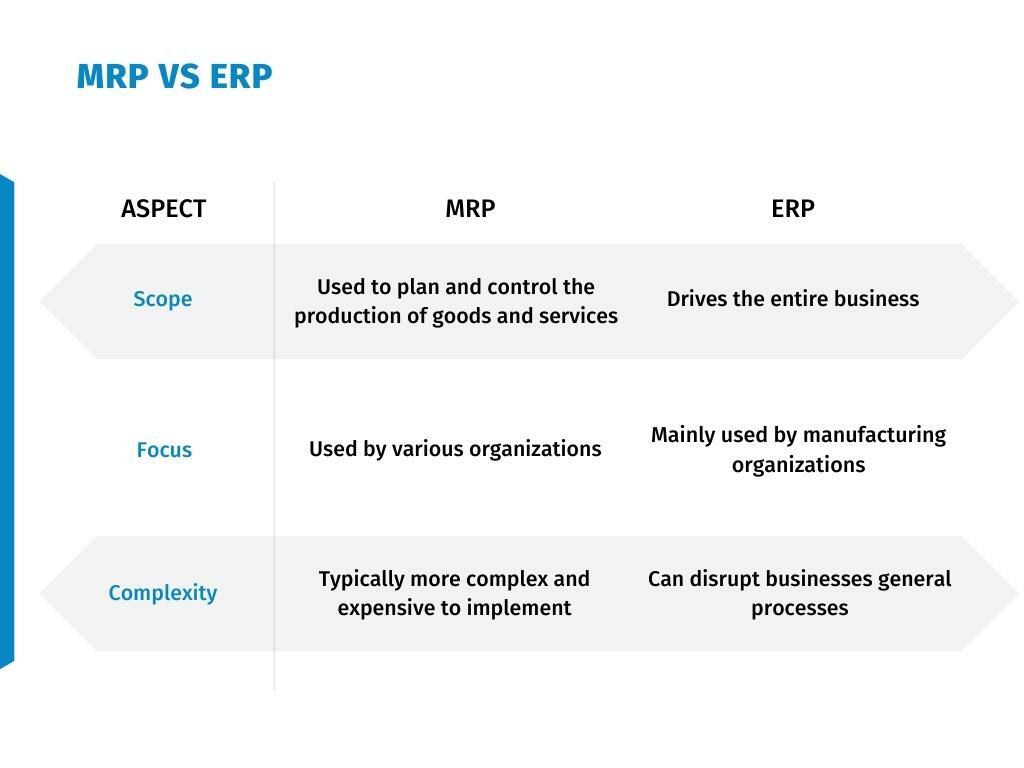
What are the key differences between MRP vs ERP system
- The significant MRP ERP difference is that MRP software is used to plan and control the production of goods and services while ERP software drives the entire business.
- ERP systems are used by various organizations while manufacturing organizations mainly use MRP systems.
- MRP systems are typically more complex and expensive to implement than general ERP systems. ERP systems can disrupt businesses general processes, while MRP systems can be less disruptive because it effects only production side.
What system is right for you – MRP or ERP, or both? How to decide?

The answer to this question depends on the specific needs of your organization. If you are a manufacturing organization, an MRP system may be better for you. An ERP system may be a better choice if you are looking for a system to operate your entire business. However, an ERP system may be a better choice if you are looking for a system to improve your financial, human resources, customer relationship, and supply chain management process.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business landscape, companies often transition from a ‘growth’ to an ‘optimization’ mindset. This strategic shift commonly occurs once a company scales significantly and aims to sustain its trajectory while enhancing operational efficiency and profitability. Here, the importance of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems cannot be understated.
Initially, a growth mindset prioritizes expansion – increasing customer base, launching new products, and broadening market reach. Conversely, the optimization mindset zeroes in on maximizing the efficiency of existing resources. In the spheres of product design and mechanical engineering, it could involve refining current designs for better efficiency or eco-friendliness instead of merely creating new products.
This is where MRP and ERP systems come into play. MRP assists in managing manufacturing processes, ensuring optimal use of materials, and minimizing waste. ERP systems, on the other hand, integrate various business functions, providing a holistic view of the organization and facilitating effective decision-making.
By enabling accurate inventory control, production planning, and schedule management, MRP and ERP systems play a vital role in the optimization process. They help businesses become more efficient, improving profit margins and boosting customer satisfaction by focusing on quality over quantity.
The optimization mindset also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, such as engineers finding cost-effective materials or designers simplifying designs without compromising user experience.
You can also find more information from our blog post about the differences between MES and ERP, and how you decide which system is best for your operations.